Data4 needed to test how to build and commission liquid-cooled high-capacity racks before offering them to customers. The operator used a proof-of-concept test to develop an industrialized version, which is now in commercial operation.
filters
Explore All Topics
Competition for grid power is increasing; data center operators need to use reserved grid power responsibly — to support business objectives, maintain strong relationships with authorities and avoid negative publicity.
The proposed Scope 2 Guidance updates radically alter current accounting methodologies. These changes will complicate Scope 2 offset markets (e.g., EACs, RECs and GOs), adding unnecessary complexity and resource demands to Scope 2 accounting.
The public wants to understand data center resource use and performance metrics. Data center operators need to propose a label format that shares appropriate performance metrics while protecting confidential information.
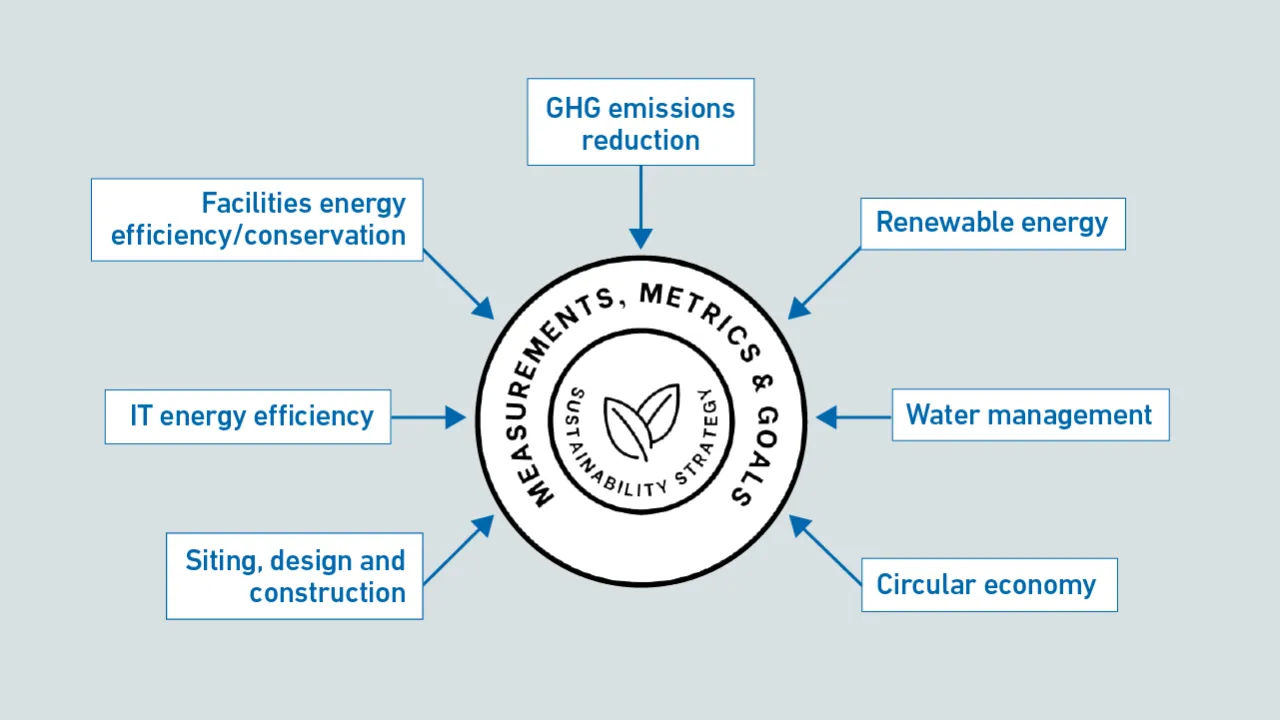
The projected tripling of data center capacity calls into question the industry's commitment to sustainability. The growth creates an opportunity to build out energy- and water-efficient infrastructure and increase carbon-free energy use.
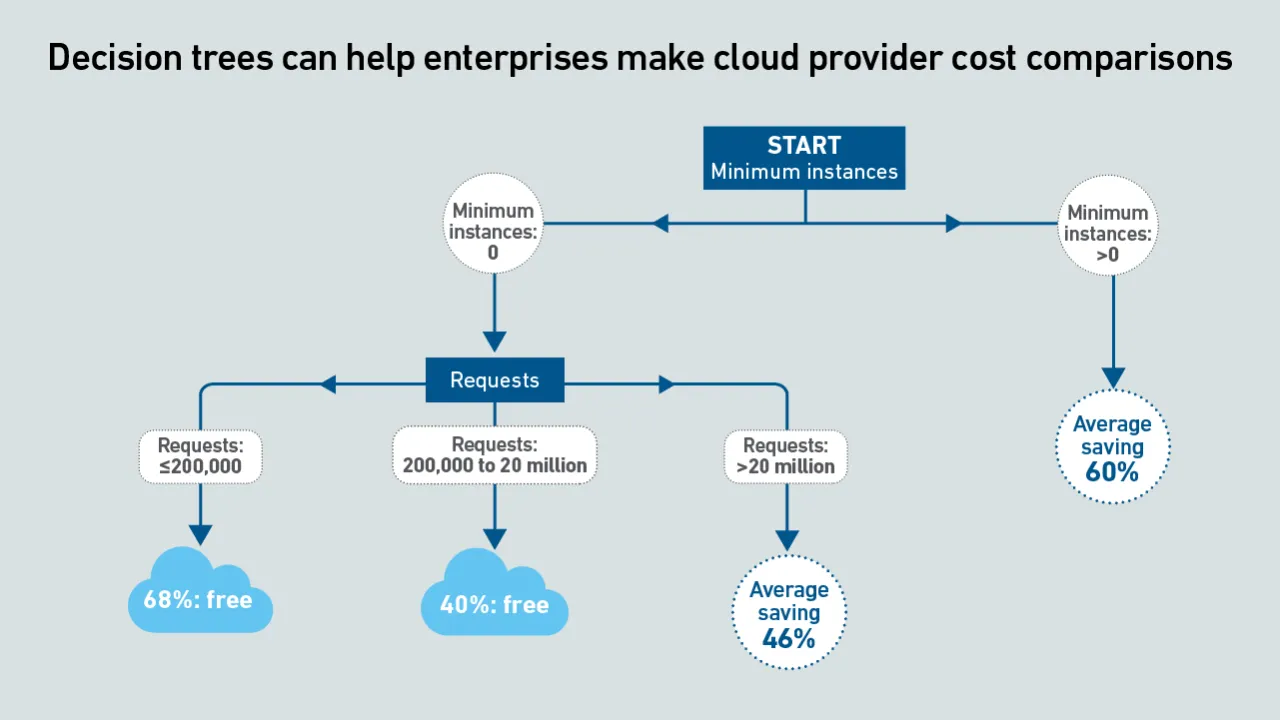
Serverless container services enable rapid scalability, which is ideal for AI inference. However, inconsistent and opaque pricing metrics hinder comparisons. This report uses machine learning to derive clear guidance by means of decision trees.
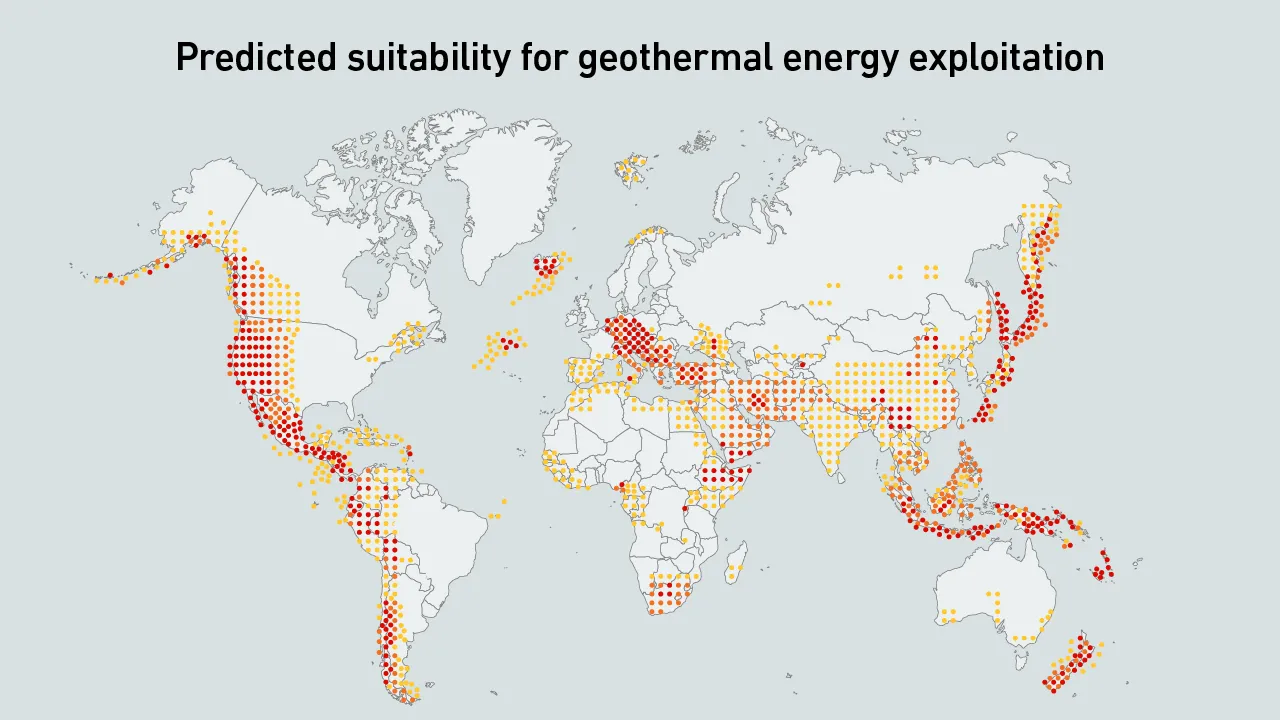
Underground hot rocks are emerging as a source of firm, low-carbon power for data centers, with new techniques expanding viable locations. Compared with nuclear, geothermal may be better positioned to support planned data center growth.
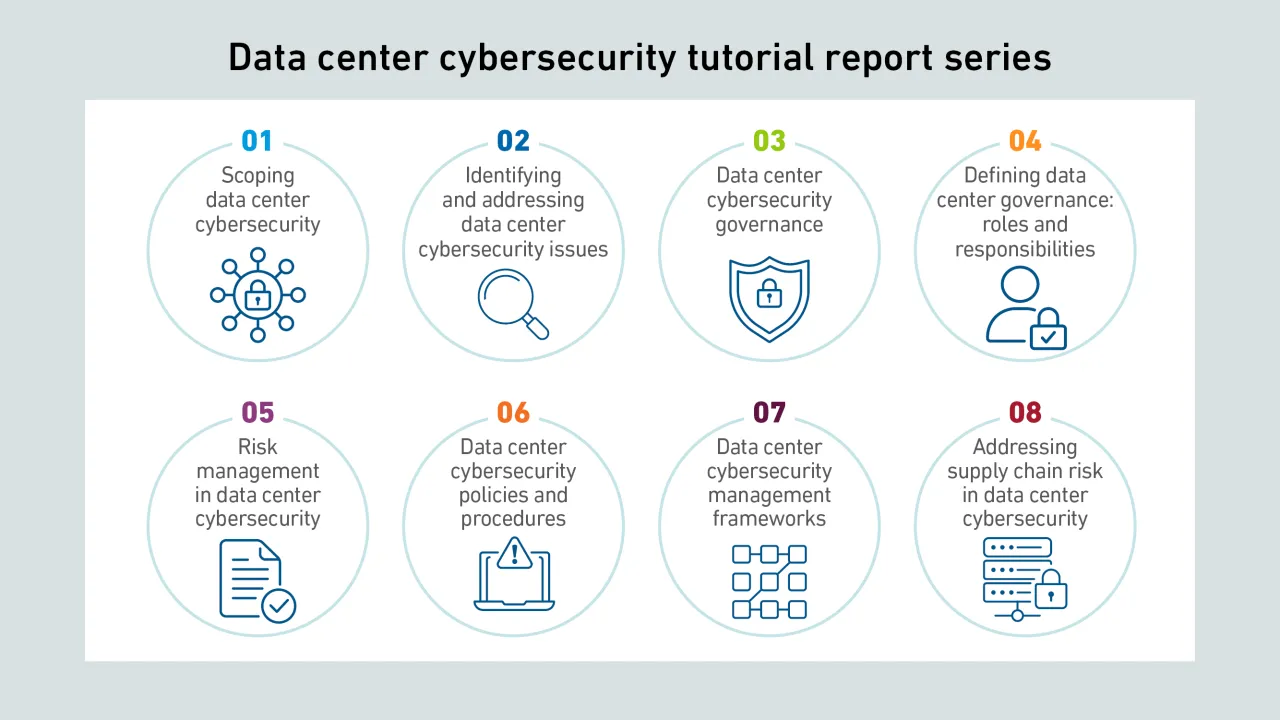
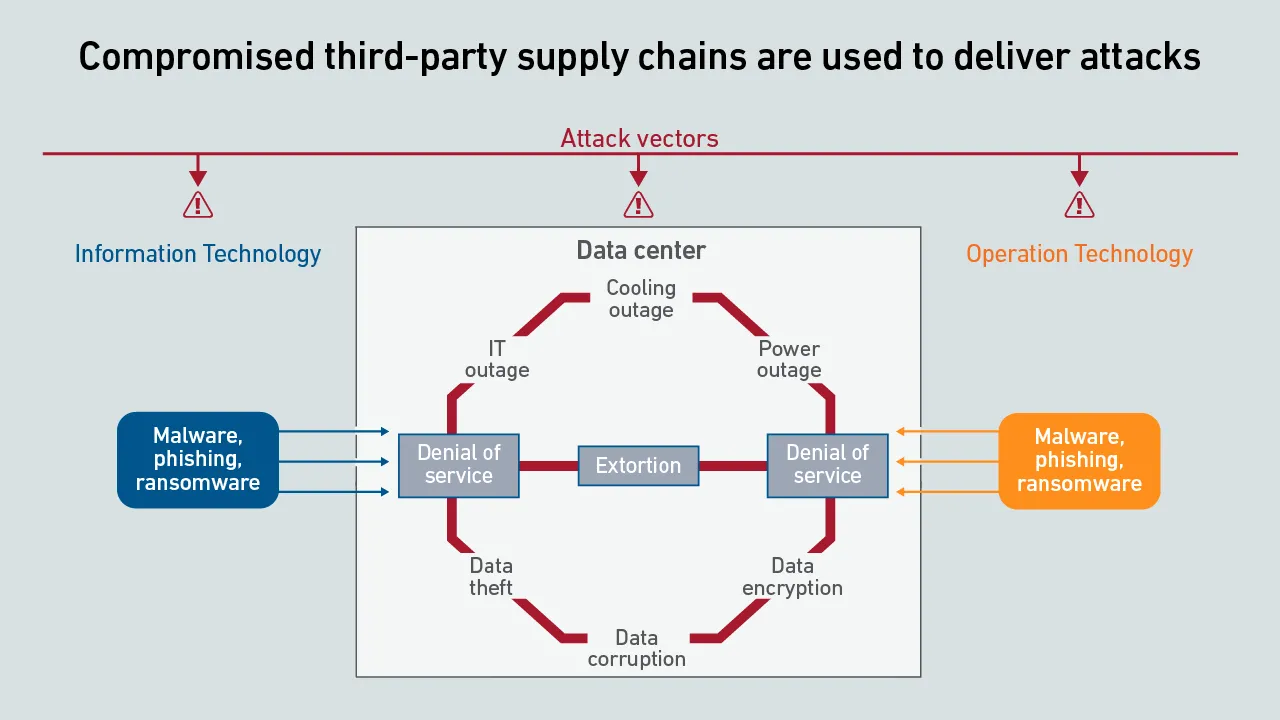
Cybersecurity has traditionally not been a key focus of attention for data center operators. But cyber incidents are on the rise and concerns are growing. Unaddressed vulnerabilities leave operators at increasing risk from evolving threats.
This briefing report identifies and describes several de facto standards and laws used in the field of data center sustainability and efficiency (for convenience, we use the term "standards" for all).
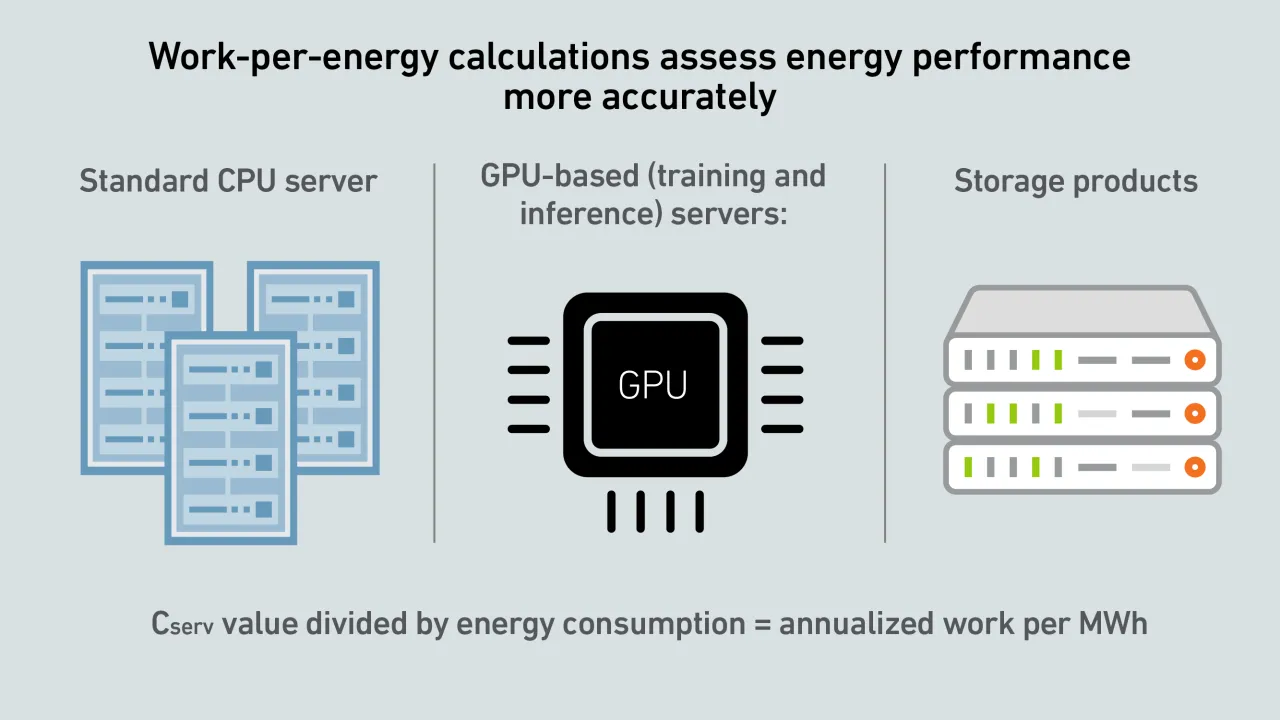
IT operators lack a credible work-per-energy metric to report overall IT and facilities system efficiency. Developments in reporting IT equipment work capacities enable the industry to begin experimenting with this metric.
The European Commission aims to ease climate risk reporting by removing mid-cap operators from CSRD's scope and delaying reports to 2028. But under current rules, 2025 reports are required and foreign-owned mid-cap operators stay covered.
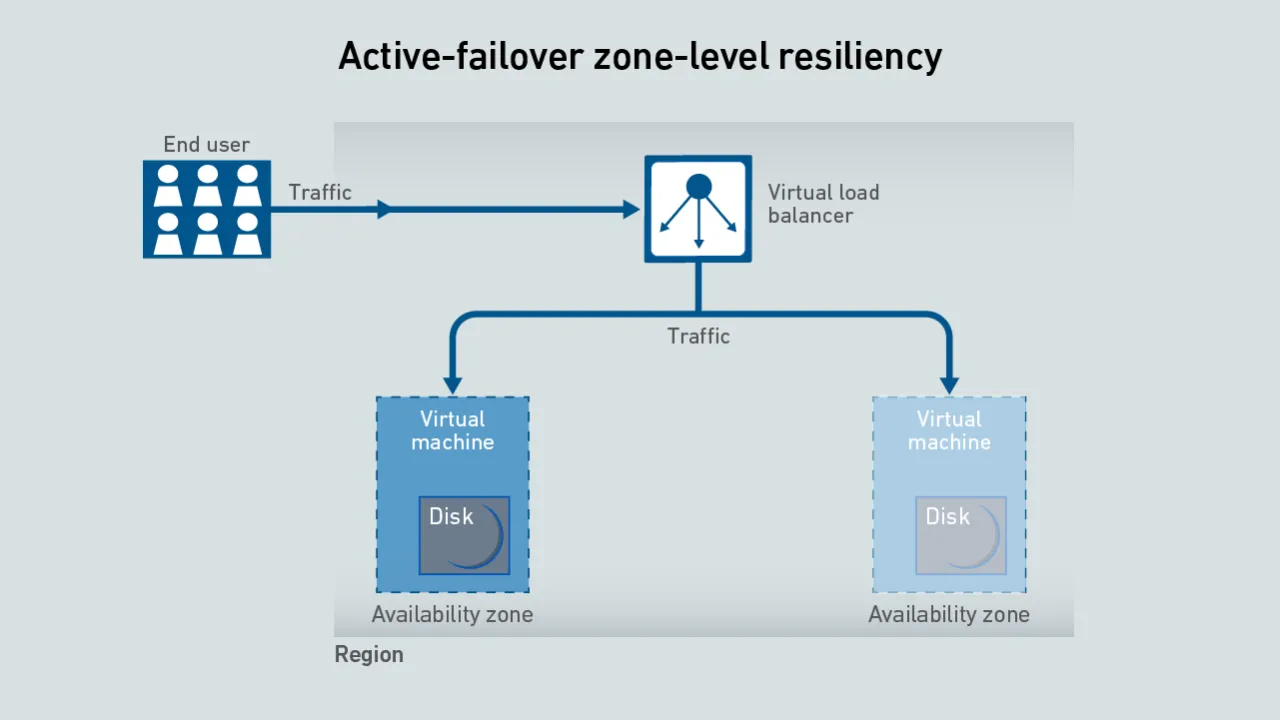
When building cloud applications, organizations cannot rely solely on cloud provider infrastructure for resiliency. Instead, they must architect their applications to survive occasional service and data center outages.
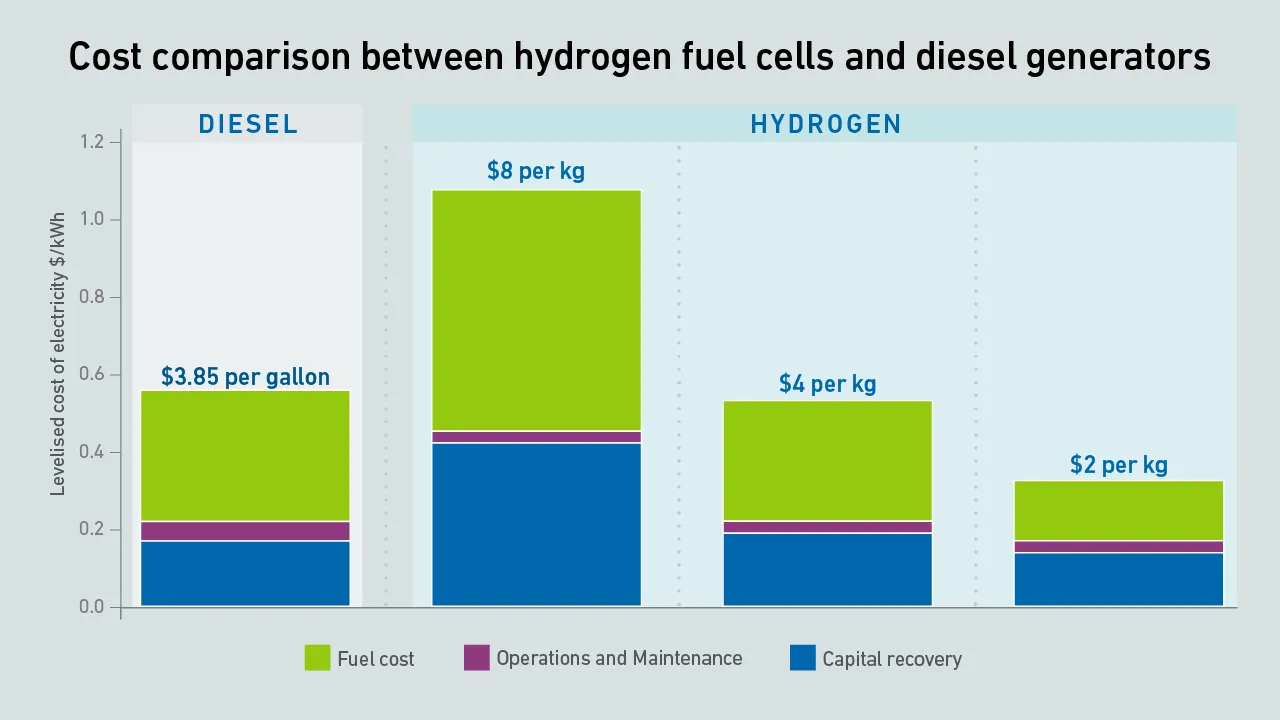
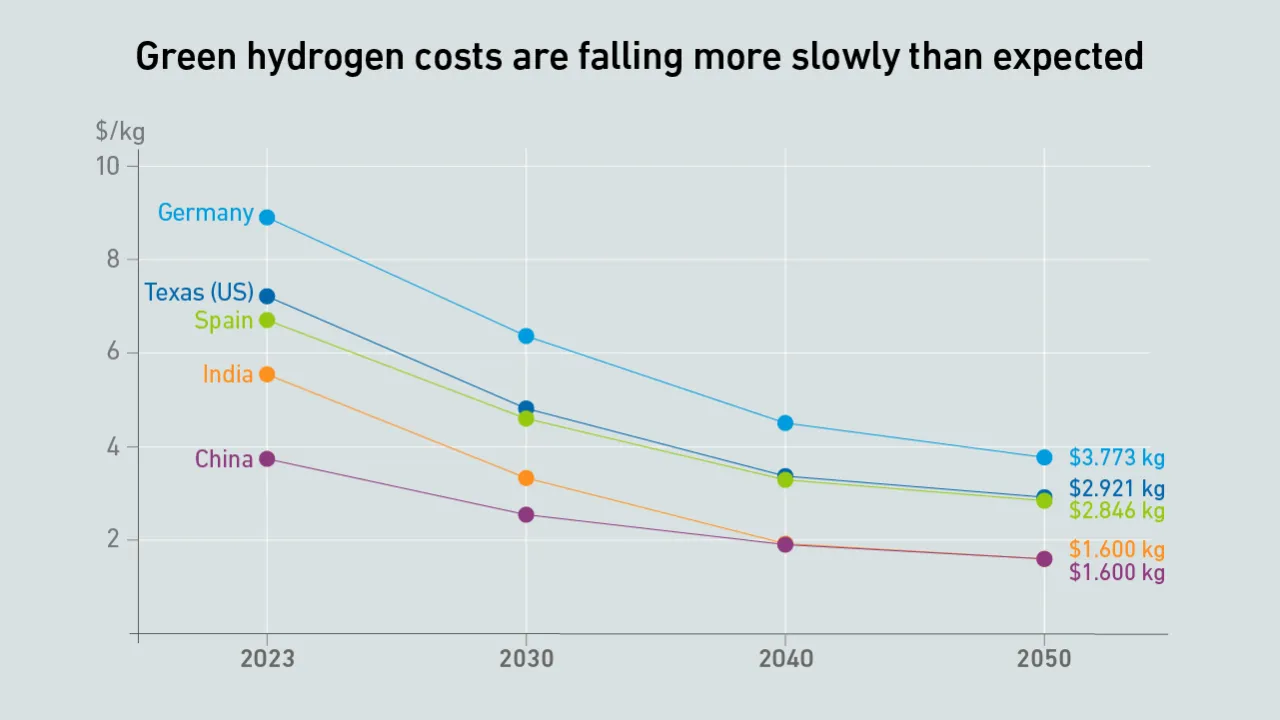
The cost of low-carbon green hydrogen will be prohibitive for primary power for many years. Some operators may adopt high-carbon (polluting) gray hydrogen ahead of transitioning to green hydrogen
Cyber strategies need to extend beyond the facility to reduce third-party supplier threat risks. Data center executives should apply robust, consistent supply chain risk management practices to critical data center technologies
Hydrogen from renewable sources is in short supply. While future plentiful supplies are planned, currently only a very small number of data centers are using hydrogen for standby power.
 Peter Judge
Peter Judge

 Dr. Tomas Rahkonen
Dr. Tomas Rahkonen

 Jay Dietrich
Jay Dietrich


 Dr. Owen Rogers
Dr. Owen Rogers
 John O'Brien
John O'Brien
 Seb Shehadi
Seb Shehadi


 Michael O'Neil
Michael O'Neil