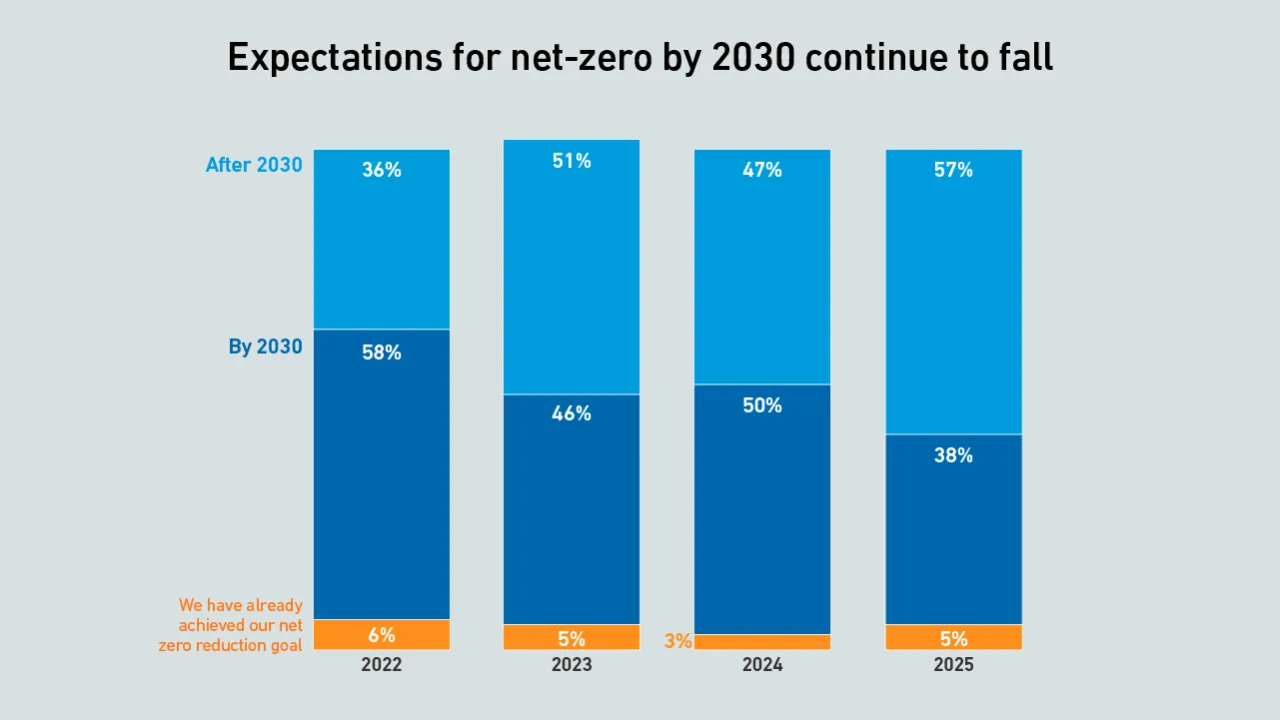
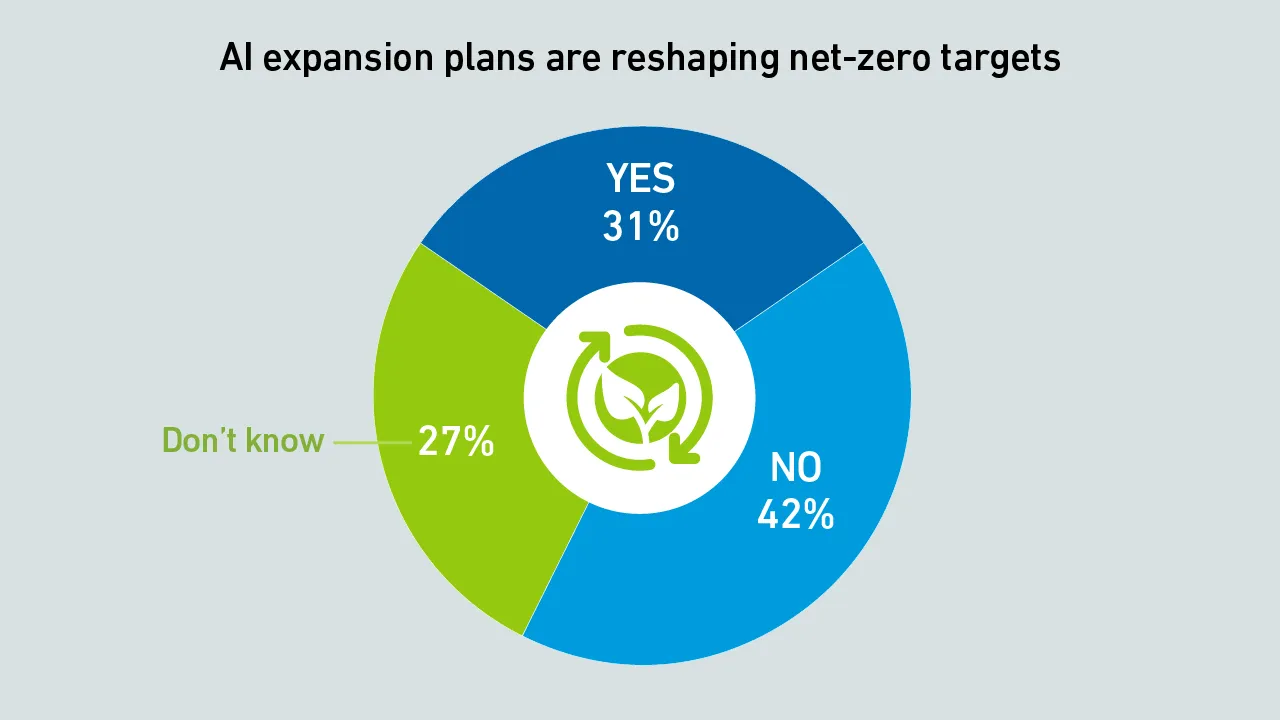
Net-zero commitments are becoming more common across the data center industry, but power demand growth and stricter carbon accounting rules are reshaping expectations.
filters
Explore All Topics
As the data center industry aims to address rising power density, technical developments in facilities are undergoing significant changes. With average rack densities climbing, new ways to configure and power data centers are increasing. To keep up…
Cloud and AI growth are straining power systems, and the US GRID Act could make expansion more difficult. The industry will need greater transparency on projected energy and water use, project plans, and incentives.
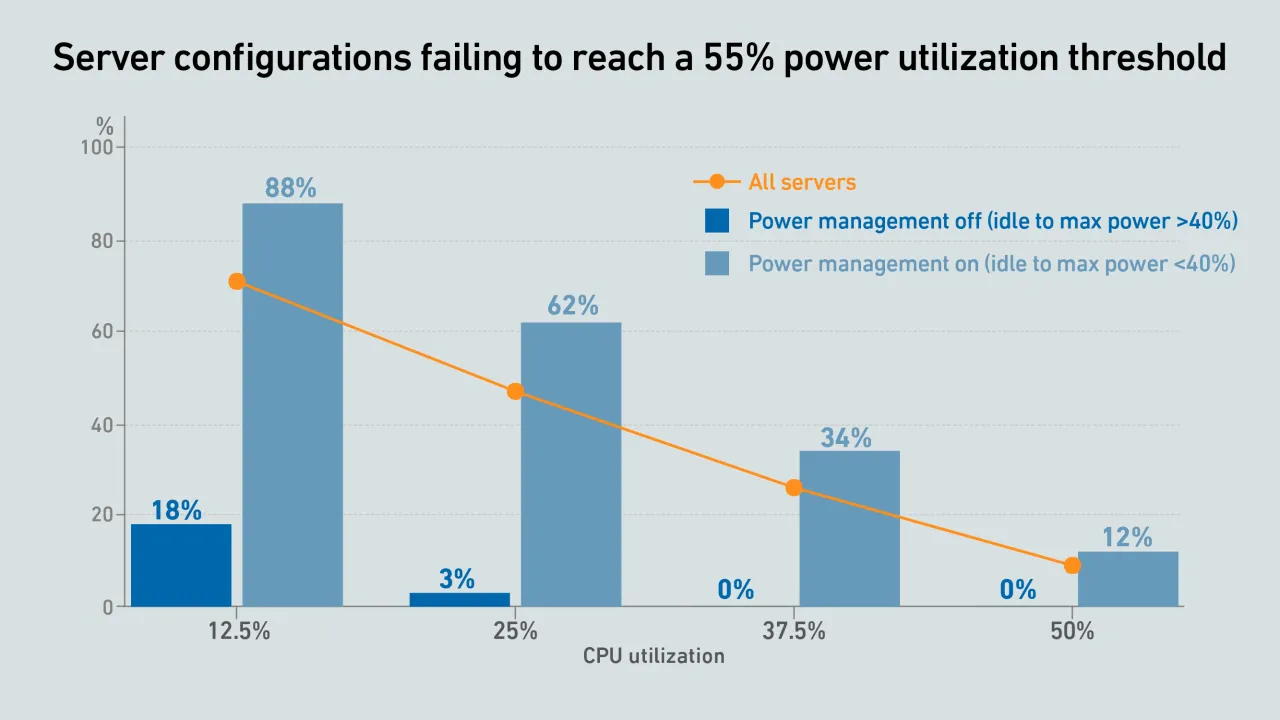
Uptime Intelligence analysis shows that minimum thresholds for IT power utilization misrepresents server work capacity utilization. These thresholds can unintentionally incentivize operators to disable server energy efficiency features.
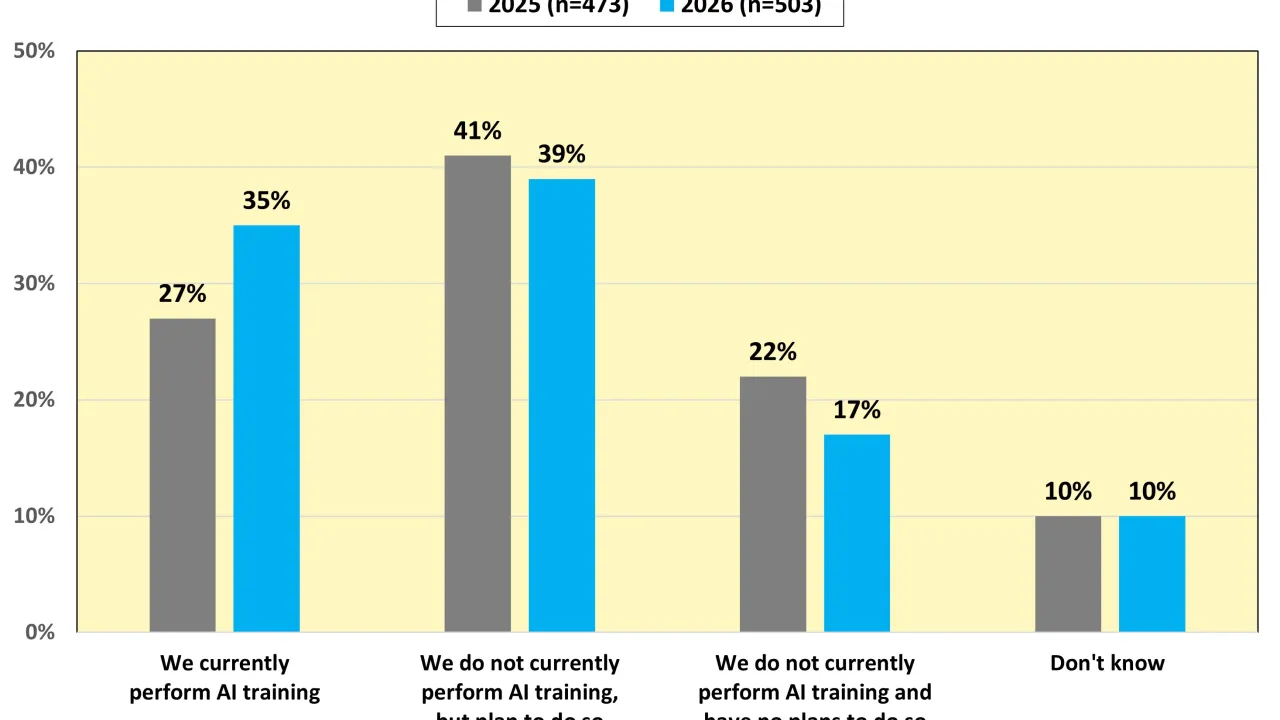
Results from Uptime Institute's 2026 AI Infrastructure Survey (n=1,141) focus on the data center infrastructure currently used or being planned to use to host AI Training and AI Inference, as well as future industry outlooks on the usage of AI. The…
Concerns over rising electricity costs and environmental impact are driving local opposition to new data center projects in the US, prompting a growing number of cancellations.
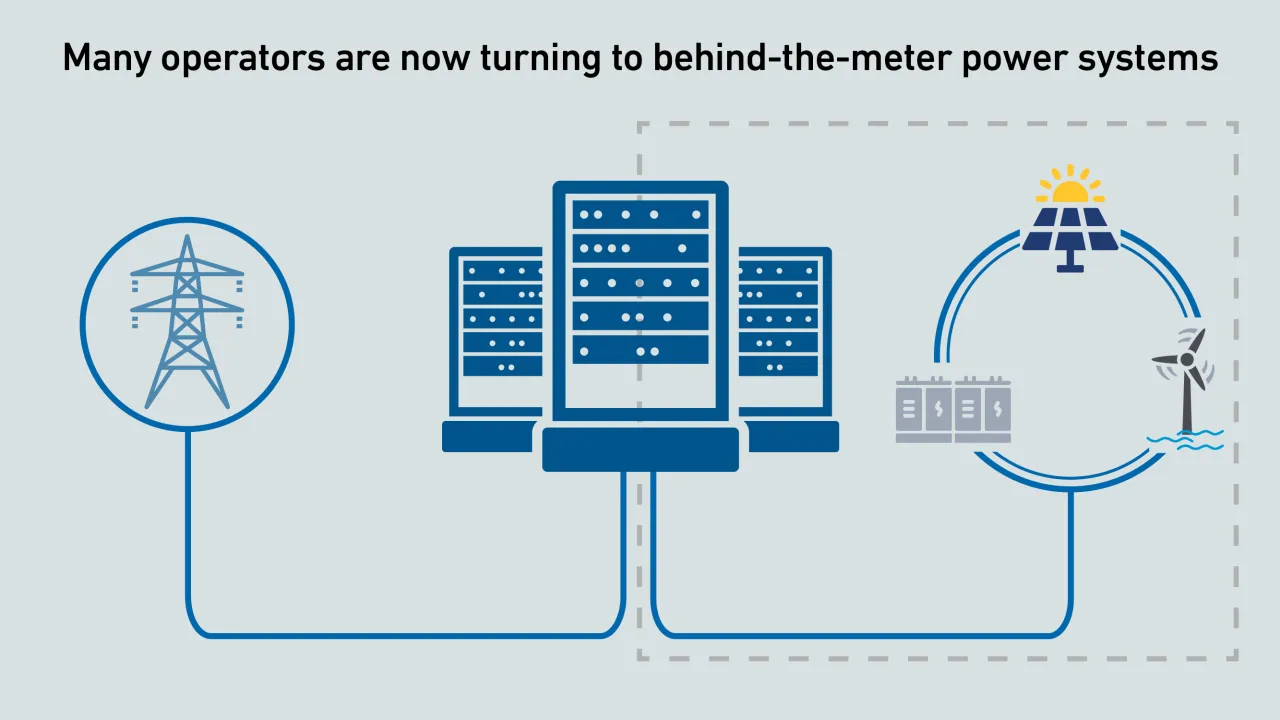
Operators are proposing behind-the-meter power systems to accelerate the buildout of new AI data center infrastructure. Executing this strategy requires regulatory changes in many jurisdictions and new data center design approaches.
While DCIM software has certain characteristics of a digital twin, persistent data quality and system interoperability issues mean a true digital twin for data center operations is still some way off.
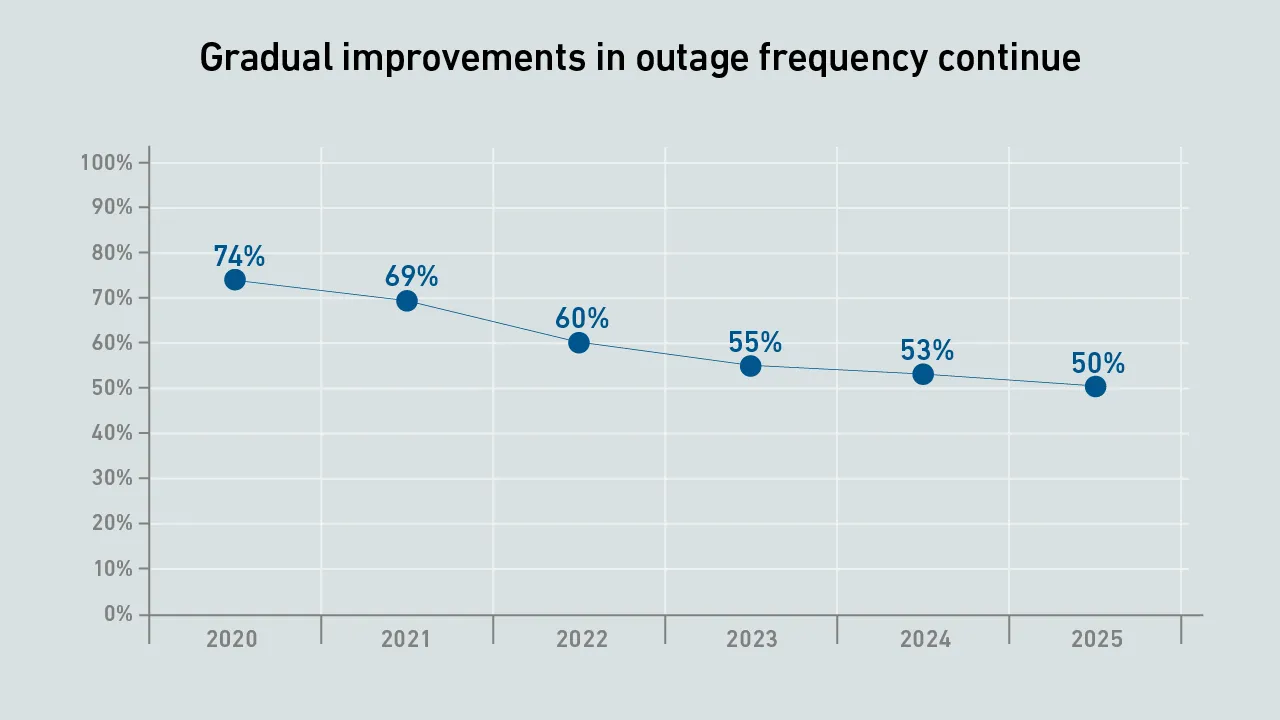
There is a growing list of reasons why designers and operators are re-examining issues around redundancy and resiliency — but for most, it is inescapable: current levels of resiliency will need to be maintained.
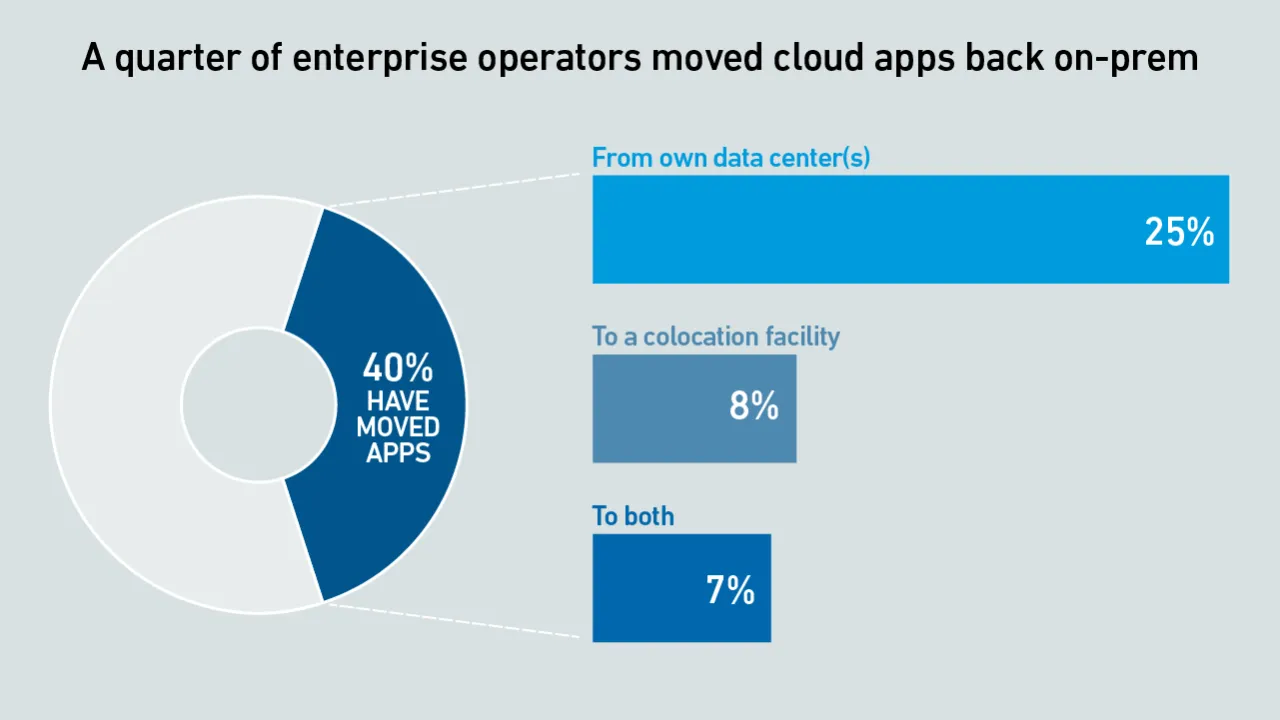
Growing workload demand continued to drive capacity growth in 2025. Results from the Uptime Institute Service Providers and Capacity Survey 2025 offer an insight into trends in capacity growth and the adoption of hybrid strategies.
French data center operators must meet strict PUE and WUE targets from early 2027 to maintain their electricity tax benefits.
Surging demand for AI data centers is driving a shift to on-site natural gas power, even though operators admit this will delay the achievement of net-zero goals.
As AI adoption spreads, most data centers will not host large training clusters — but many will need to operate specialized systems to run inferencing close to applications.
Elon Musk's merger of his SpaceX aerospace company with his AI firm xAI has relit the thrusters under the concept of building big data centers in space. However, the technical difficulties involved may ultimately thwart his ambitions.
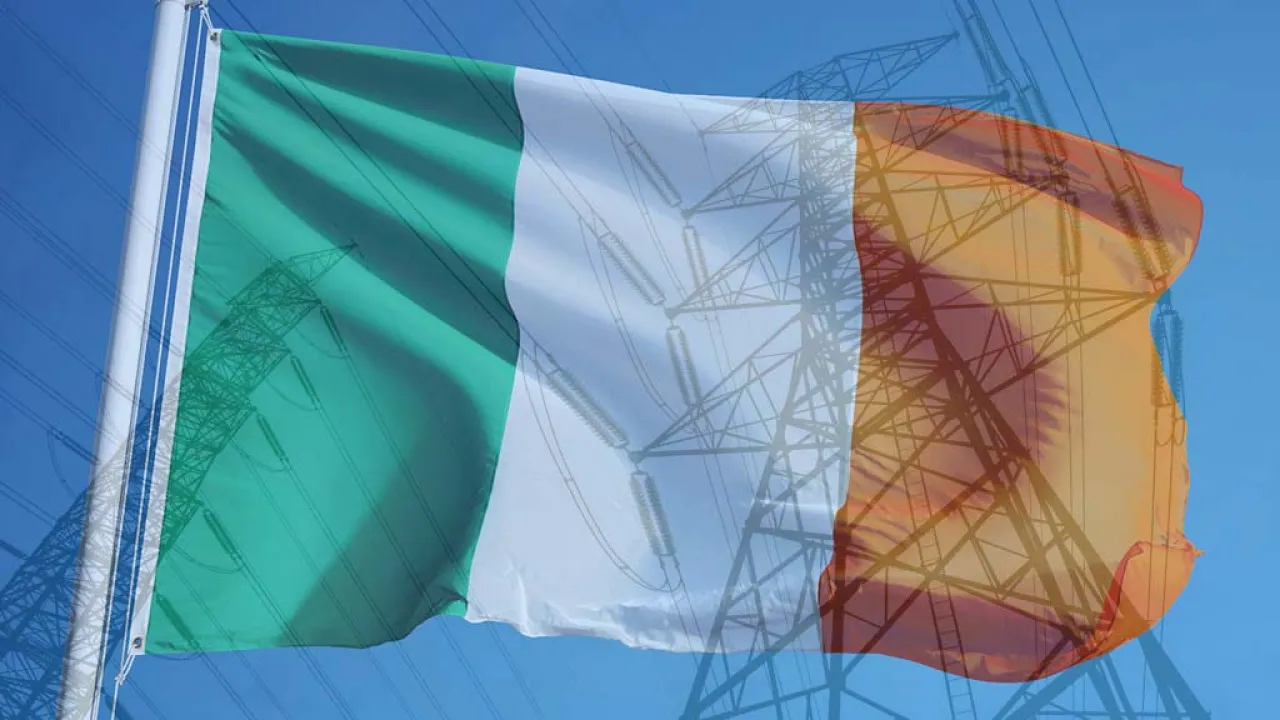
Ireland has issued new conditions for large grid loads and proposed new codes for data center connections; similar measures are expected to follow in other locations.
 Douglas Donnellan
Douglas Donnellan
 Daniel Bizo
Daniel Bizo
 Chris Brown
Chris Brown

 Jay Dietrich
Jay Dietrich

 Dr. Tomas Rahkonen
Dr. Tomas Rahkonen

 Paul Carton
Paul Carton
 Anthony Sbarra
Anthony Sbarra
 Laurie Williams
Laurie Williams
 Max Smolaks
Max Smolaks

 John O'Brien
John O'Brien
 Andy Lawrence
Andy Lawrence
 Rose Weinschenk
Rose Weinschenk
 Peter Judge
Peter Judge
 Dr. Owen Rogers
Dr. Owen Rogers