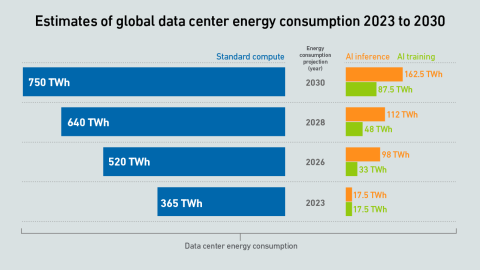
Training large transformer models is different from all other workloads — data center operators need to reconsider their approach to both capacity planning and safety margins across their infrastructure.
filters
Explore All Topics
The US government’s AI compute diffusion rules, introduced in January 2025, will be rescinded — with new rules coming. It warns any dealings linked to advanced Chinese chips will require US export authorization. Operators still face tough demands.
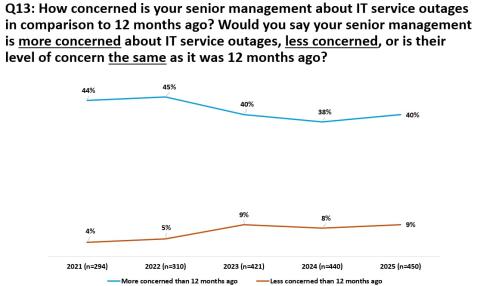
Results from Uptime Institute's 2025 Data Center Resiliency Survey (n=970) focus on data center resiliency issues and the impact of outages on the data center sector globally.The attached data files below provide full results of the survey,…
High-end AI systems receive the bulk of the industry’s attention, but organizations looking for the best training infrastructure implementation have choices. Getting it right, however, may take a concerted effort.
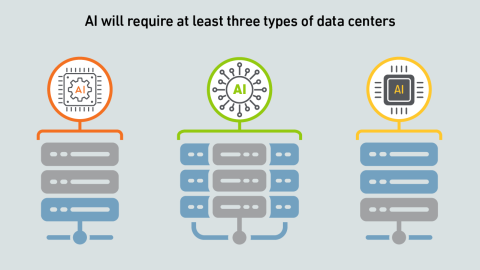
AI is not a uniform workload — the infrastructure requirements for a particular model depend on a multitude of factors. Systems and silicon designers envision at least three approaches to developing and delivering AI.
Agentic AI offers enormous potential to the data center industry over the next decade. But are the benefits worth the inevitable risks?
The emergence of the Chinese DeepSeek LLM has raised many questions. In this analysis, Uptime Intelligence considers some of the implications for all those primarily concerned with the deployment of AI infrastructure.
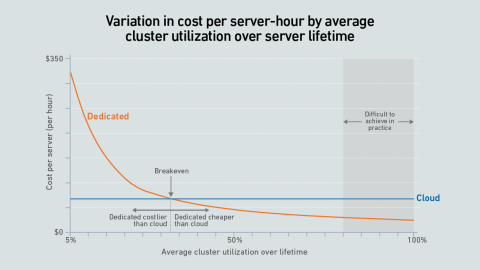
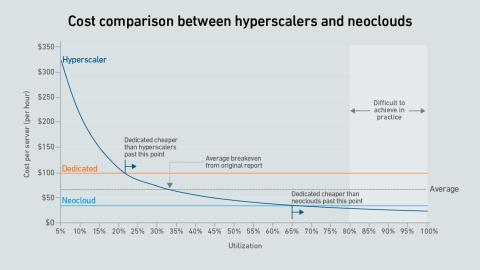
A new wave of GPU-focused cloud providers is offering high-end hardware at prices lower than those charged by hyperscalers. Dedicated infrastructure needs to be highly utilized to outperform these neoclouds on cost.
The US government is applying a new set of rules to control the building of large AI clusters around the world. The application of these rules will be complex.
The data center industry’s growth projections can be met by combining energy supply growth and demand reduction. Highly utilized IT infrastructure and efficient software can mitigate demand growth while delivering needed IT capacity.
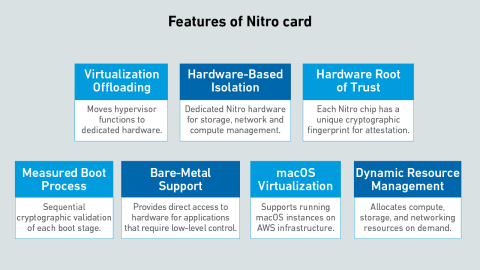
Hyperscalers design their own servers and silicon to scale colossal server estates effectively. AWS uses a system called Nitro to offload virtualization, networking and storage management from the server processor onto a custom chip.
If adopted, the UNEP U4E server and storage product technical specifications may create a confusing and counter-productive regulatory structure. The current proposals are as likely to limit as improve data center operations' efficiency
Dedicated GPU infrastructure can beat the public cloud on cost. Companies considering purchasing an AI cluster need to consider utilization as the key variable in their calculations.
Supersized generative AI models are placing onerous demands on both IT and facilities infrastructure. The challenge for next-generation AI infrastructure will be power, forcing operators to explore new electrification architectures.
Nvidia’s dominant position in the AI hardware market may be steering data center design in the wrong direction. This dominance will be harder to sustain as enterprises begin to understand AI and opt for cheaper, simpler hardware.
 Daniel Bizo
Daniel Bizo


 Paul Carton
Paul Carton
 Anthony Sbarra
Anthony Sbarra
 Laurie Williams
Laurie Williams

 Max Smolaks
Max Smolaks
 John O'Brien
John O'Brien
 Andy Lawrence
Andy Lawrence

 Dr. Owen Rogers
Dr. Owen Rogers
 Peter Judge
Peter Judge
 Jay Dietrich
Jay Dietrich