Training large transformer models is different from all other workloads — data center operators need to reconsider their approach to both capacity planning and safety margins across their infrastructure.
filters
Explore All Topics
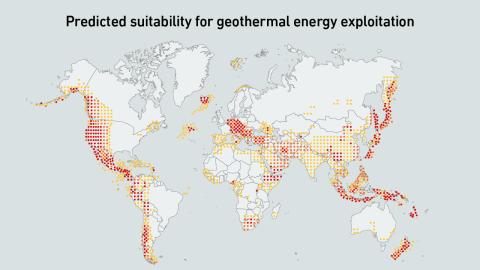
Underground hot rocks are emerging as a source of firm, low-carbon power for data centers, with new techniques expanding viable locations. Compared with nuclear, geothermal may be better positioned to support planned data center growth.
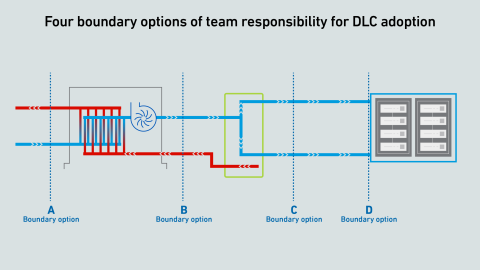
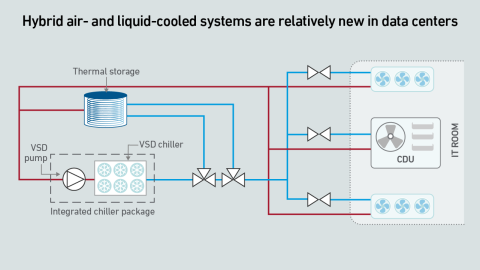
Direct liquid cooling challenges the common “line of demarcation” for responsibilities between facilities and IT teams. Operators lack a consensus on a single replacement model—and this fragmentation may persist for several years.
Join Uptime experts as they discuss and answer questions on grid demands and sustainability strategies while debating how to meet decarbonization goals. This is a member and subscriber-only event.
For the past 15 years, the case for moving workloads out of enterprise data centers and into the cloud and colocation has been strong. Power availability and demand for high-density capacity may change that.
To meet the demands of unprecedented rack power densities, driven by AI workloads, data center cooling systems need to evolve and accommodate a growing mix of air and liquid cooling technologies.
Today, GPU designers pursue outright performance over power efficiency. This is a challenge for inference workloads that prize efficient token generation. GPU power management features can help, but require more attention.
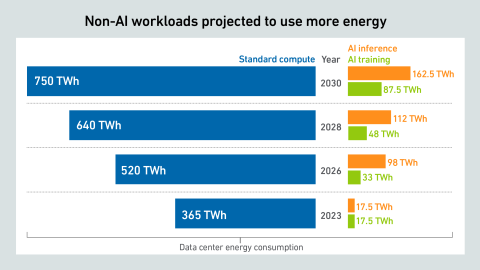
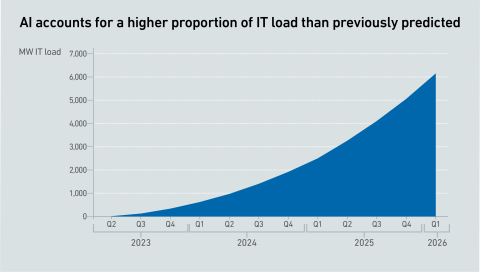
The past year warrants a revision of generative AI power estimates, as GPU shipments have skyrocketed, despite some offsetting factors. However, uncertainty remains high, with no clarity on the viability of these spending levels.
Many operators expect GPUs to be highly utilized, but examples of real-world deployments paint a different picture. Why are expensive compute resources being wasted — and what effect does this have on data center power consumption?
While AI infrastructure build-out may focus on performance today, over time data center operators will need to address efficiency and sustainability concerns.
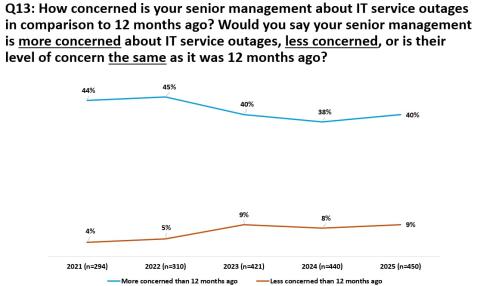
Results from Uptime Institute's 2025 Data Center Resiliency Survey (n=970) focus on data center resiliency issues and the impact of outages on the data center sector globally.The attached data files below provide full results of the survey,…
How far can we go with air? Uptime experts discuss and answer questions on cooling strategies and debate the challenges and trade-offs with efficiency and costs.Please watch this latest entry in the Uptime Intelligence Client Webinar series. The…
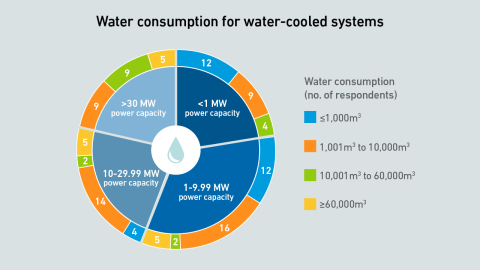
Critics argue that data center water use is excessive and poorly managed. Operators should select a cooling system to fit the local climate and available water supply, explaining water use within the context of local conditions.
High-end AI systems receive the bulk of the industry’s attention, but organizations looking for the best training infrastructure implementation have choices. Getting it right, however, may take a concerted effort.
Compared with most traditional data centers, those hosting large AI training workloads require increased attention to dynamic thermal management, including capabilities to handle sudden and substantial load variations effectively.
 Daniel Bizo
Daniel Bizo

 Peter Judge
Peter Judge
 Jacqueline Davis
Jacqueline Davis
 Max Smolaks
Max Smolaks
 Jay Dietrich
Jay Dietrich
 Jay Paidipati
Jay Paidipati
 Andy Lawrence
Andy Lawrence
 Tomas Rahkonen
Tomas Rahkonen


 Paul Carton
Paul Carton
 Anthony Sbarra
Anthony Sbarra
 Laurie Williams
Laurie Williams
 Muhammad Naveed Saeed
Muhammad Naveed Saeed