The shortage of DRAM and NAND chips caused by demands of AI data centers is likely to last into 2027, making every server more expensive.
filters
Explore All Topics
Microsoft and other major campus operators are increasing transparency on new projects and committing to absorb their full development costs, but further commitments are needed to fully address public concerns.
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang's comment that liquid-cooled AI racks will need no chillers created some turbulence — however, the concept of a chiller-free data center is an old one and is unlikely to suit most operators.
AI in data center operations is shifting from experimentation to early production use. Adoption remains cautious and bounded, focused on practical automation that supports operators rather than replacing them.
In 2026, enterprises will be more realistic about their use of generative AI, prioritizing simple use cases that deliver clear, timely value over those more innovative projects where returns — and successful outcomes — are less assured.
Investment in large-scale AI has accelerated the development of electrical equipment, which creates opportunities for data center designers and operators to rethink power architectures.
Is your infrastructure prepared for the demands of artificial intelligence? Discover how to create resilient, adaptable, and scalable systems that can meet the intensive requirements of modern AI applications. In this engaging session, Uptime's…
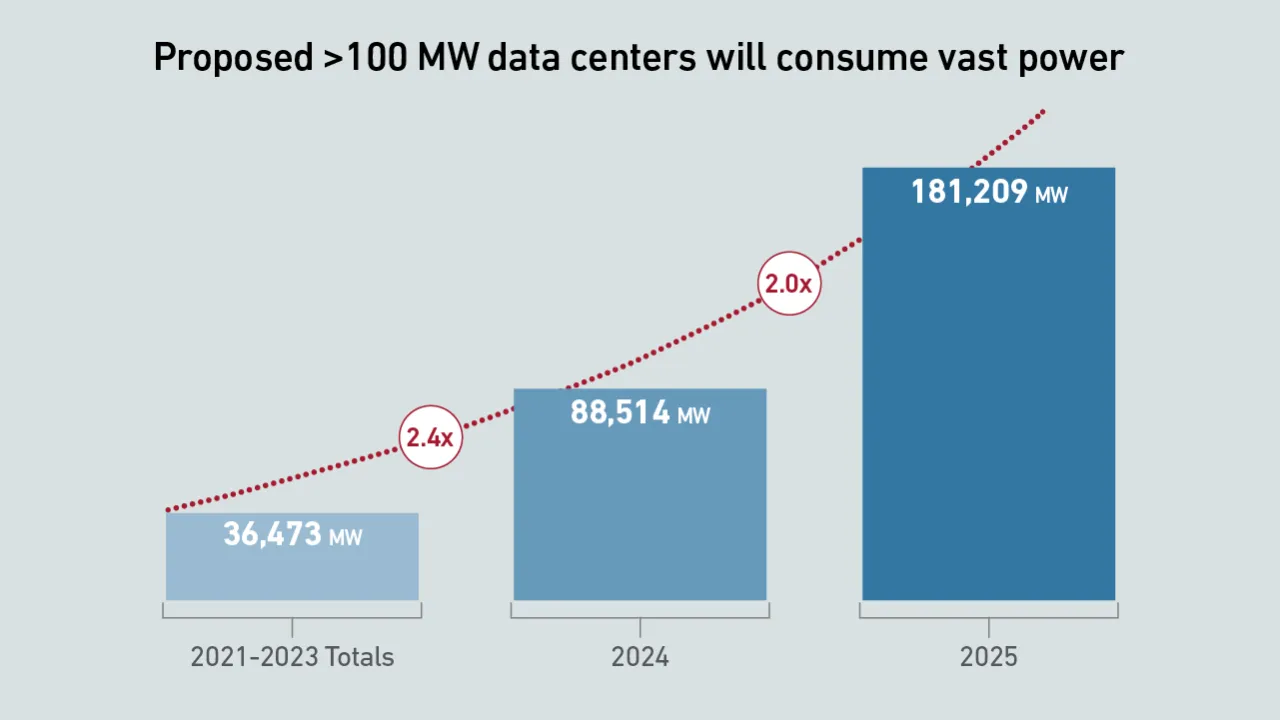
Data from Uptime Intelligence's giant data center analysis indicates that proposed power capacity and investment tied to giant data centers and campuses are at unprecedented levels.
The European Commission plans to finalize the Energy Efficiency Directive (EED) delegated regulations on June 10, 2026. The draft amendments may increase the quantity of reportable EED information and establish a data center labeling program.
DLC was developed to handle high heat loads from densified IT. True mainstream DLC adoption remains elusive; it still awaits design refinements to address outstanding operational issues for mission-critical applications.
The use of on-site natural gas power generation for big data centers will strain operators’ ability to meet net-zero carbon goals. To counter this, operators will increasingly explore, promote and in some cases deploy carbon capture and storage.
European national grid operators are advised to adopt proposed grid code requirements to protect their infrastructure from risks, such as data center activity, even though Commission action on the issue has stalled.
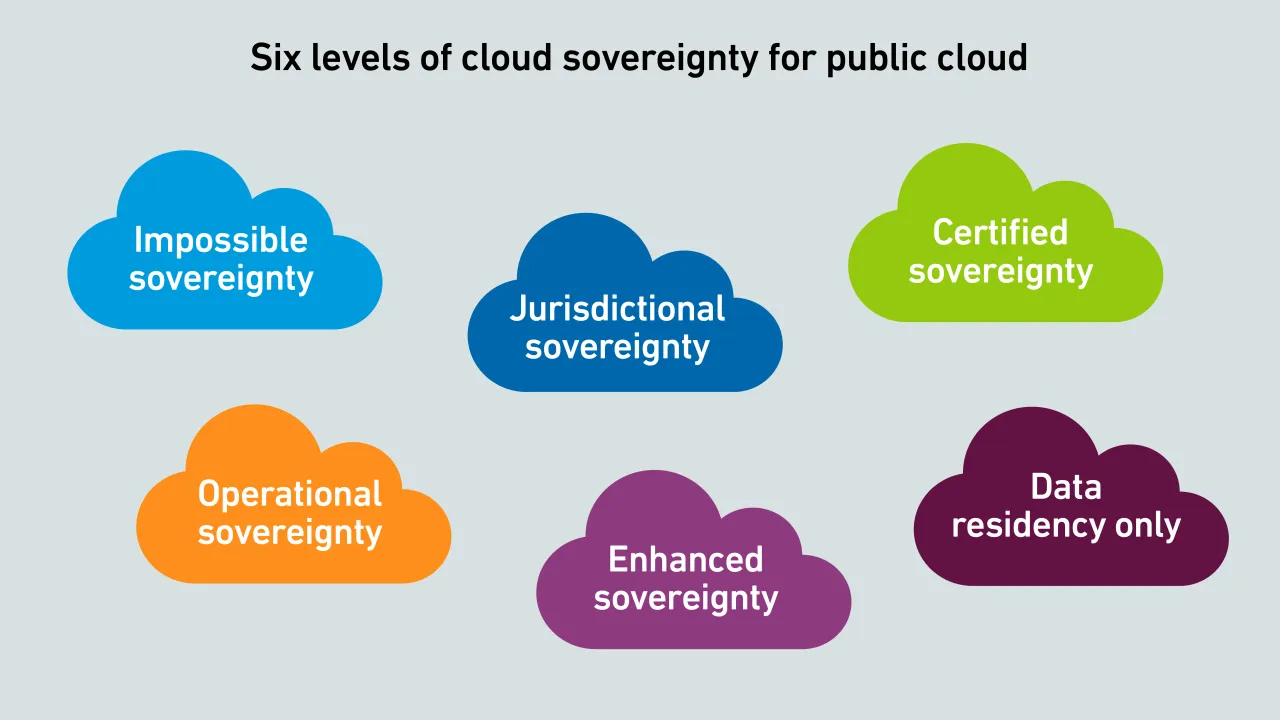
Cloud sovereignty is often treated as binary choice, but, in reality, it is a spectrum shaped by law, operations, technologies and supply chains. This framework explains the differences between sovereign public cloud options.
In this webinar and report, Uptime Intelligence looks beyond the more obvious trends of 2026 and examines some of the latest developments and challenges shaping the industry. AI is transforming data center strategies, but its impact remains uneven…
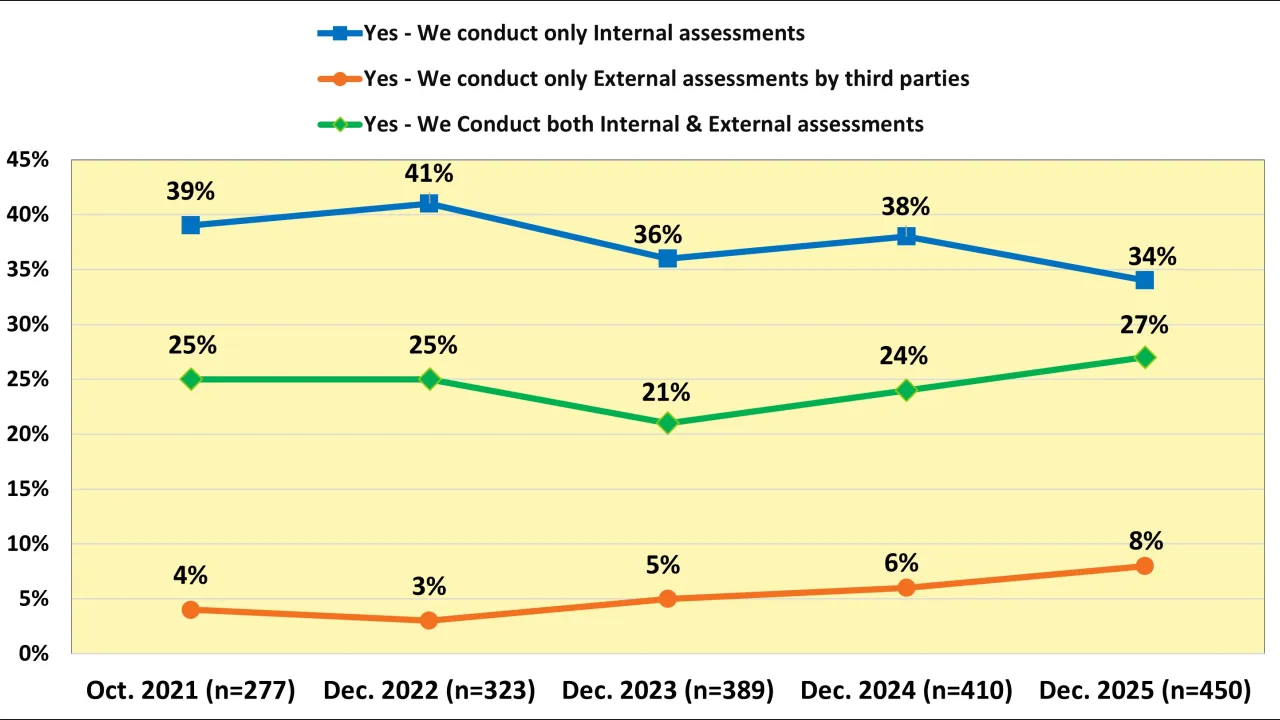
Uptime Institute's Sustainability and Climate Change Survey (n=1,054) benchmarks the data center industry in areas such as sustainability assessments, responses to extreme weather events, and how operators are handling regulatory requirements.The…
 Max Smolaks
Max Smolaks
 Jay Dietrich
Jay Dietrich
 Daniel Bizo
Daniel Bizo
 Dr. Rand Talib
Dr. Rand Talib

 Dr. Owen Rogers
Dr. Owen Rogers

 Chris Brown
Chris Brown
 Muhammad Naveed Saeed
Muhammad Naveed Saeed

 John O'Brien
John O'Brien

 Jacqueline Davis
Jacqueline Davis


 Peter Judge
Peter Judge
 Andy Lawrence
Andy Lawrence
 Douglas Donnellan
Douglas Donnellan

 Paul Carton
Paul Carton
 Anthony Sbarra
Anthony Sbarra
 Laurie Williams
Laurie Williams