Current geopolitical tensions are eroding some European organizations' confidence in the security of hyperscalers; however, moving away from them entirely is not practically feasible.

Dr. Owen Rogers
Dr. Owen Rogers is Uptime Institute’s Senior Research Director of Cloud Computing. Dr. Rogers has been analyzing the economics of cloud for over a decade as a chartered engineer, product manager and industry analyst. Rogers covers all areas of cloud, including AI, FinOps, sustainability, hybrid infrastructure and quantum computing.
orogers@uptimeinstitute.com
Latest Research
As AI workloads surge, managing cloud costs is becoming more vital than ever, requiring organizations to balance scalability with cost control. This is crucial to prevent runaway spend and ensure AI projects remain viable and profitable.
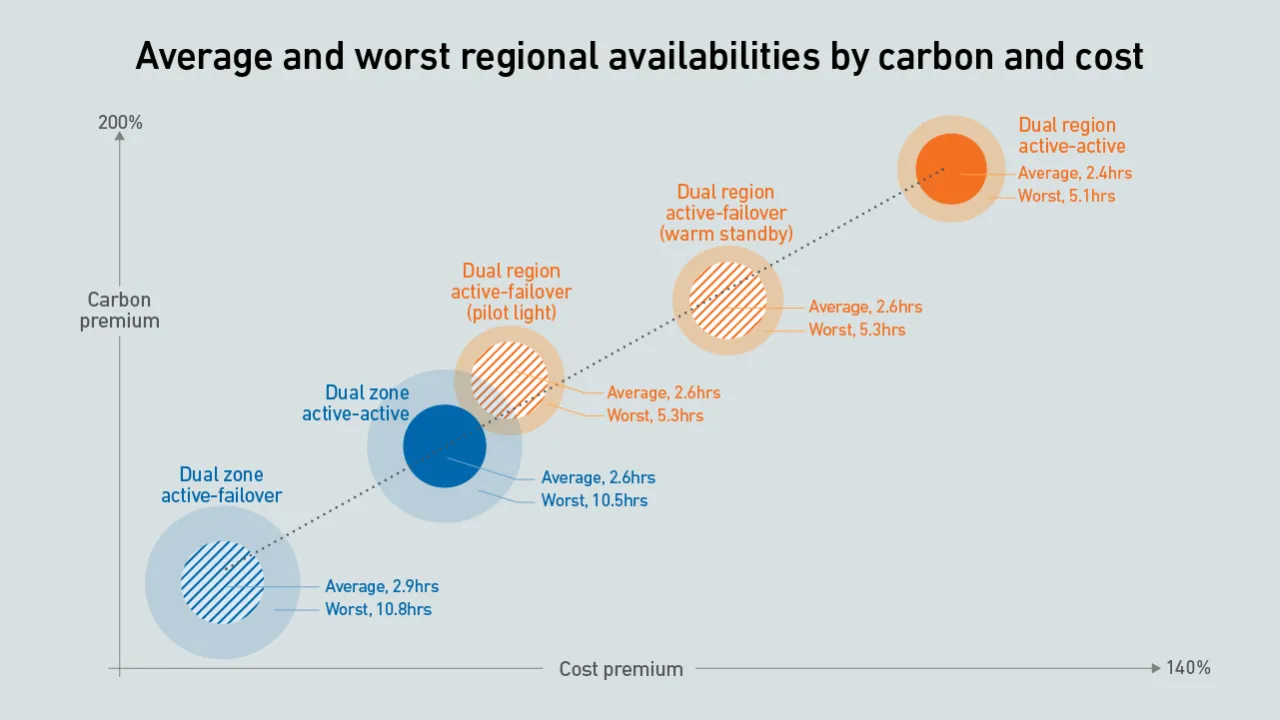
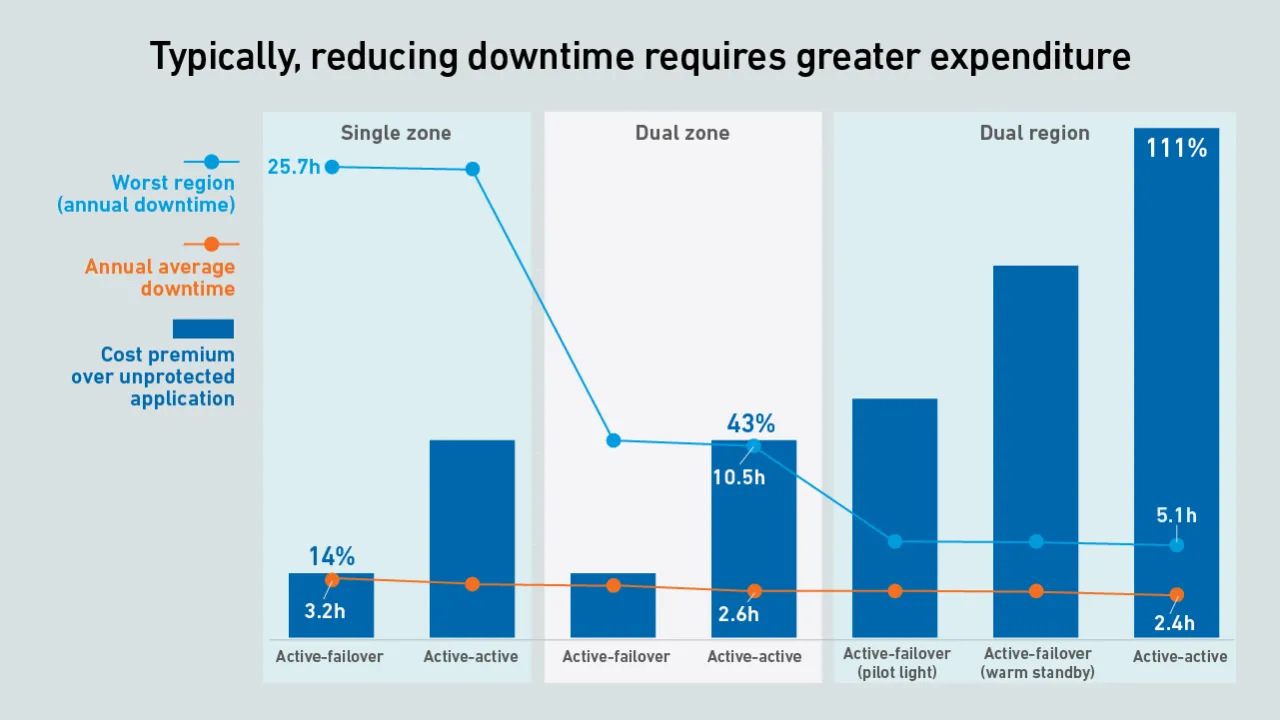
Organizations that architect resiliency into their cloud applications should expect a sharp rise in carbon emissions and costs. Some architectures provide a better compromise on cost, carbon and availability than others.
Preventing outages continues to be a central focus for data center owners and operators. While infrastructure design and resiliency frameworks have improved in many cases, the complexity of modern architectures continues to present new risks that…
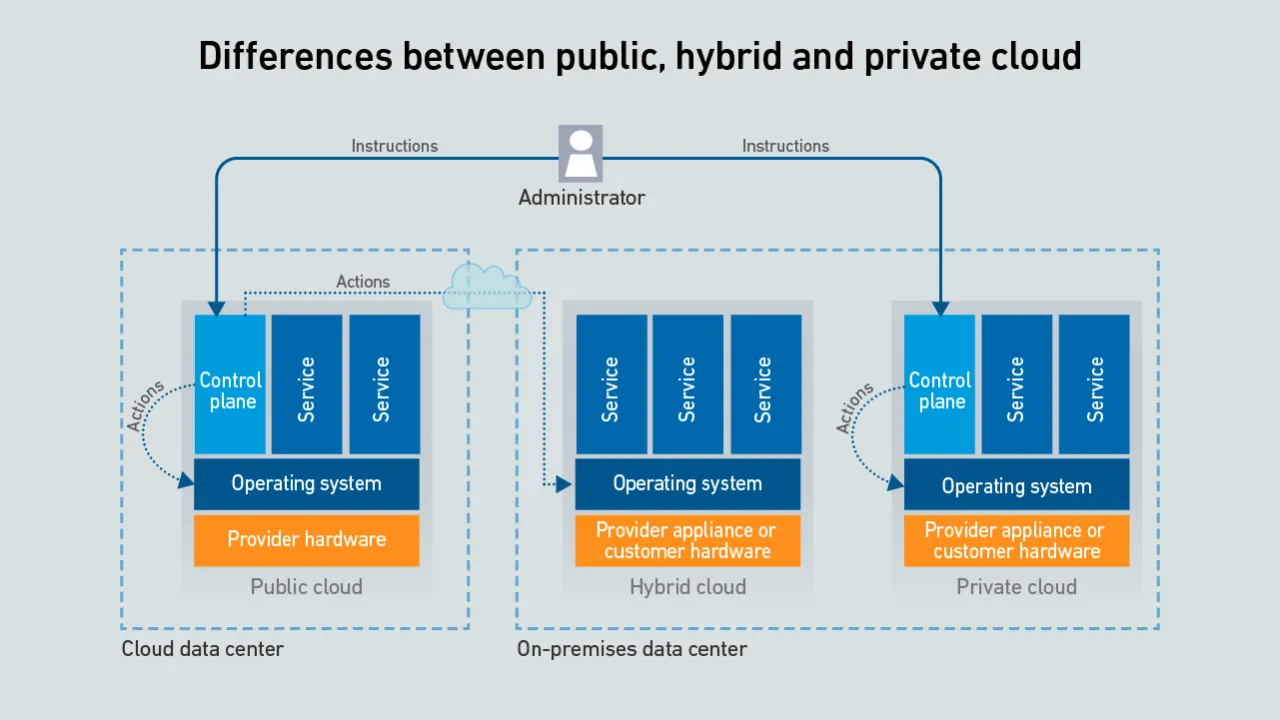
Hyperscalers offer a confusing array of on-premises versions of their public cloud-enabling infrastructure - the differences between them are rooted in whether the customer or the provider manages the control plane and server hardware.
Cloud providers live and die based on trust - customers rely on them to run workloads effectively, offer scalable capacity, sustain prices and keep data confidential. But recent geopolitical instability threatens to undermine that trust.
Quantum computing progress is slow; press releases often fail to convey the work required to make practical quantum computers a reality. Data center operators do not need to worry about quantum computing right now.
Customers are responsible for architecting resiliency into their cloud apps. However, the cloud's consumption model means resiliency comes at a price. Enterprises must evaluate availability against cost before building on the cloud.
The high capital and operating costs of infrastructure for AI mean an outage can have a significant financial impact due to lost training hours
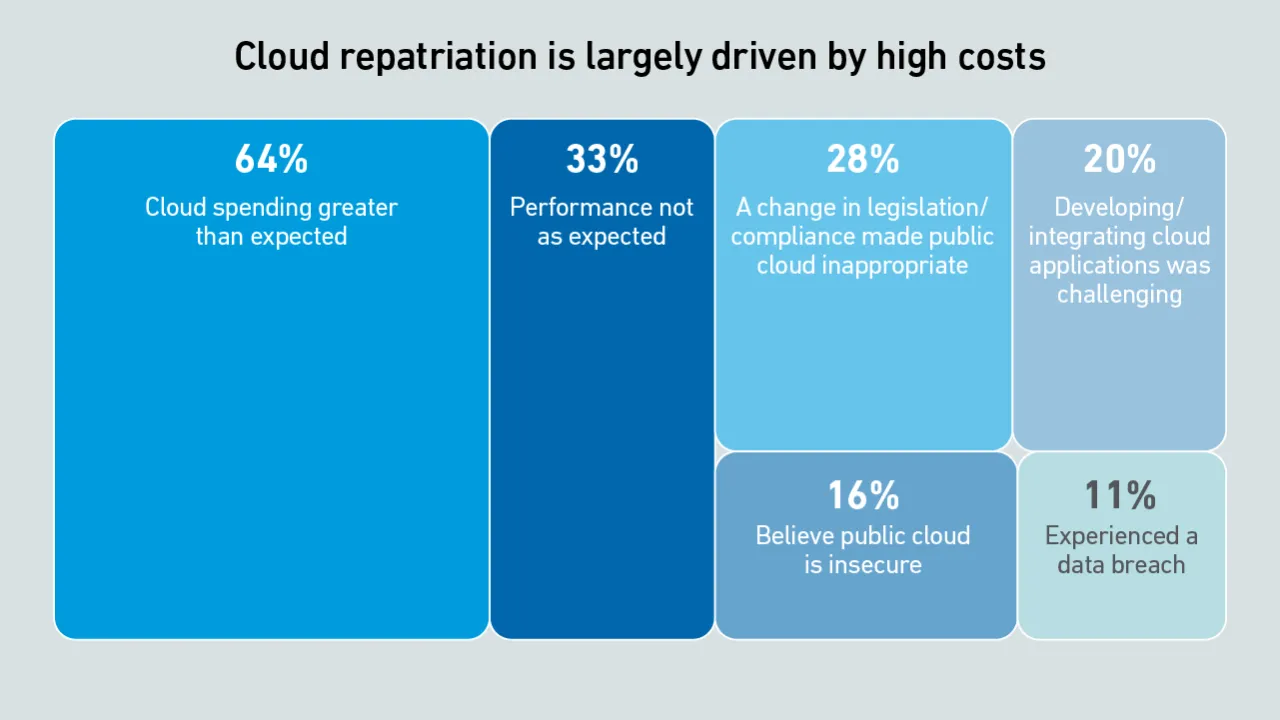
Scalability and cost efficiency are the top reasons enterprises migrate to the cloud, but scalability issues due to application design flaws can lead to spiralling costs - and some workload repatriation to on-premises facilities
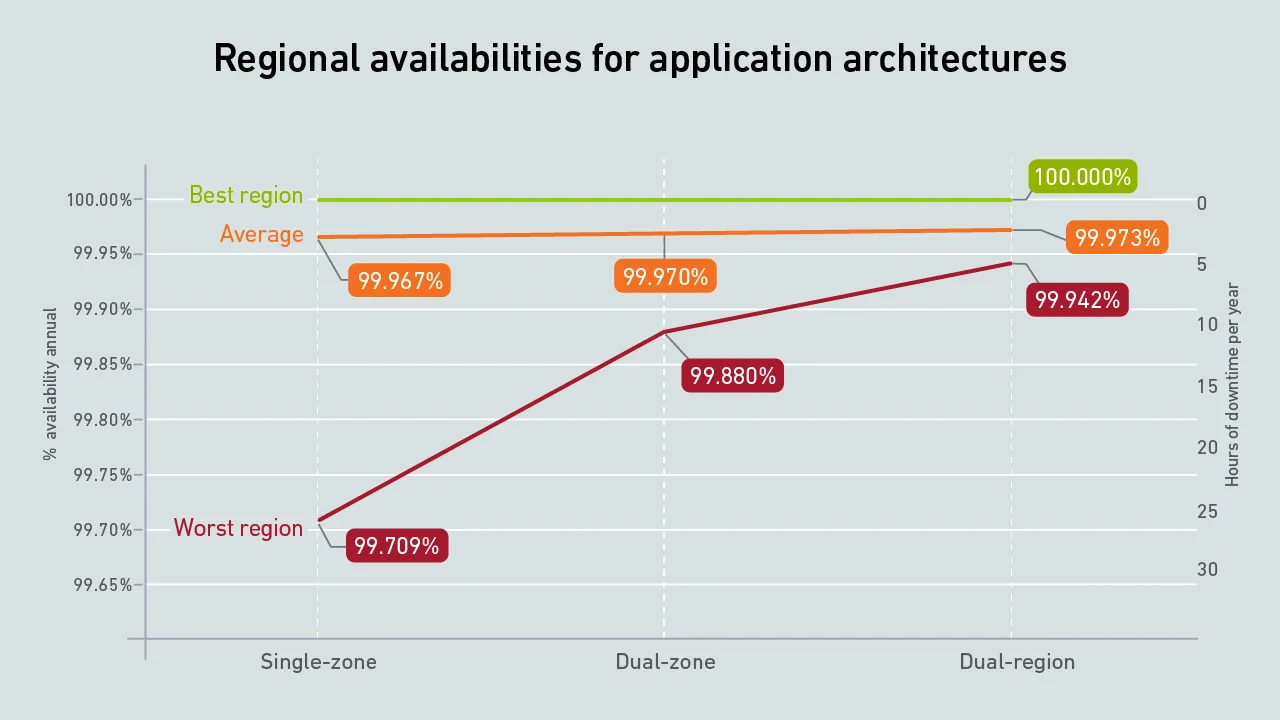
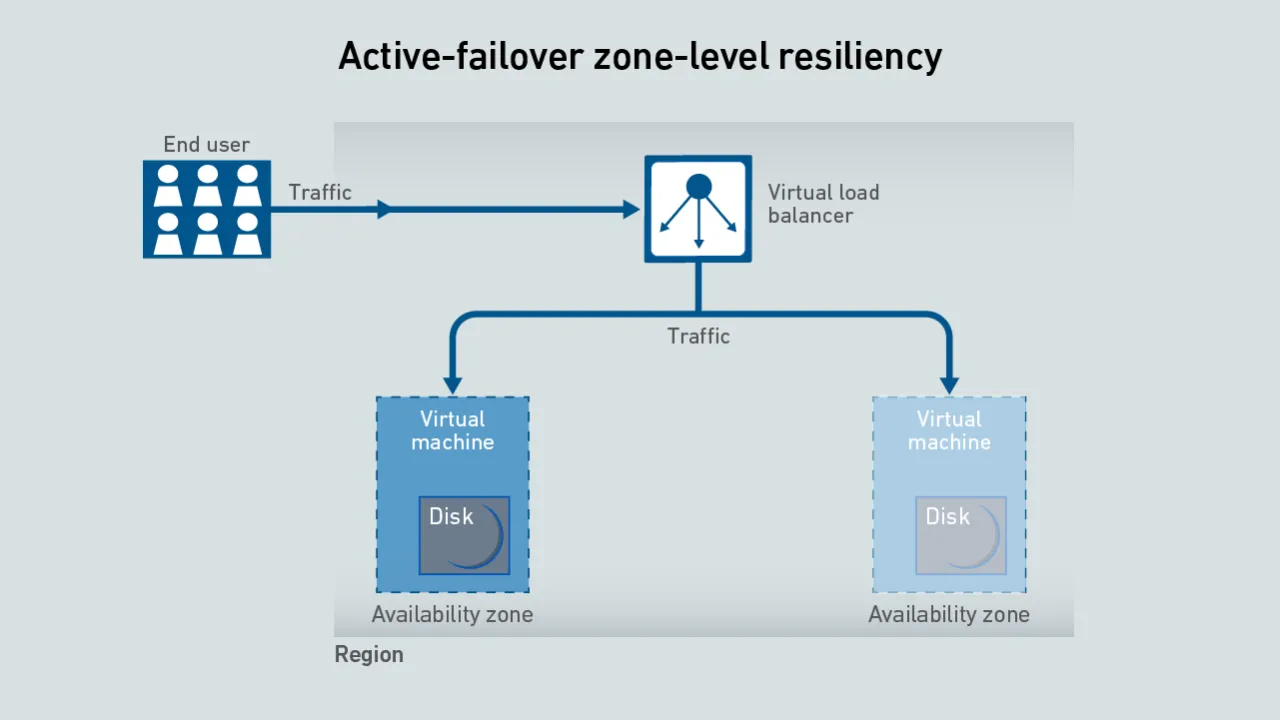
On average, cloud apps achieve availabilities of 99.97% regardless of their architecture. However, for the unlucky few that experience issues, a dual-region design has five times less downtime than one based on a single data center.
When building cloud applications, organizations cannot rely solely on cloud provider infrastructure for resiliency. Instead, they must architect their applications to survive occasional service and data center outages.
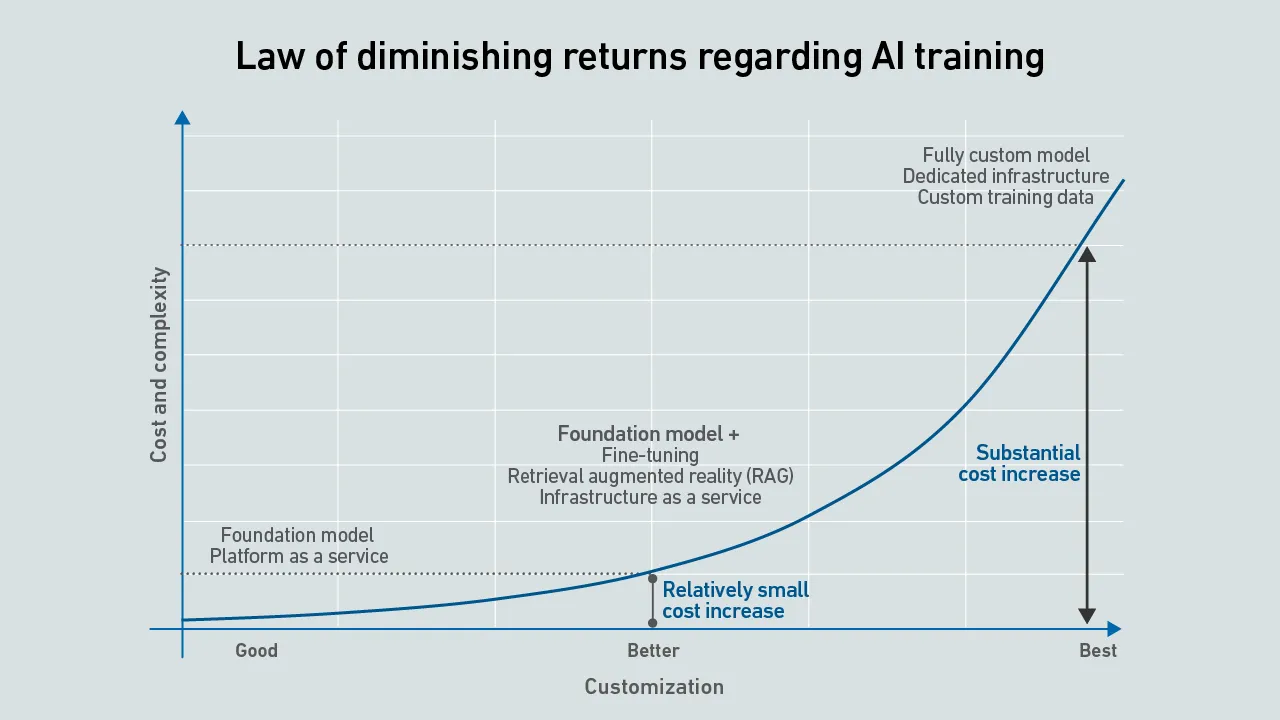
Dedicated AI infrastructure helps ensure data is controlled, compliant and secure, while models remain accurate and differentiated. However, this reassurance comes at a cost that may not be justified compared with cheaper options.
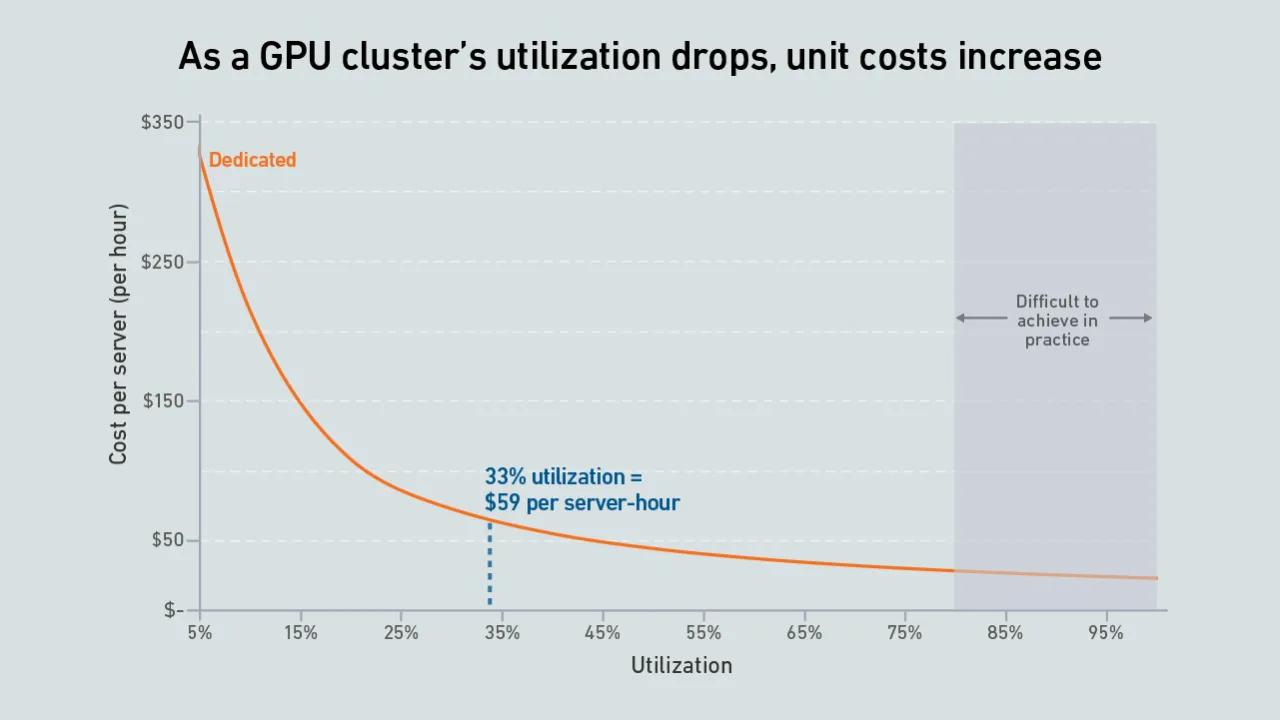
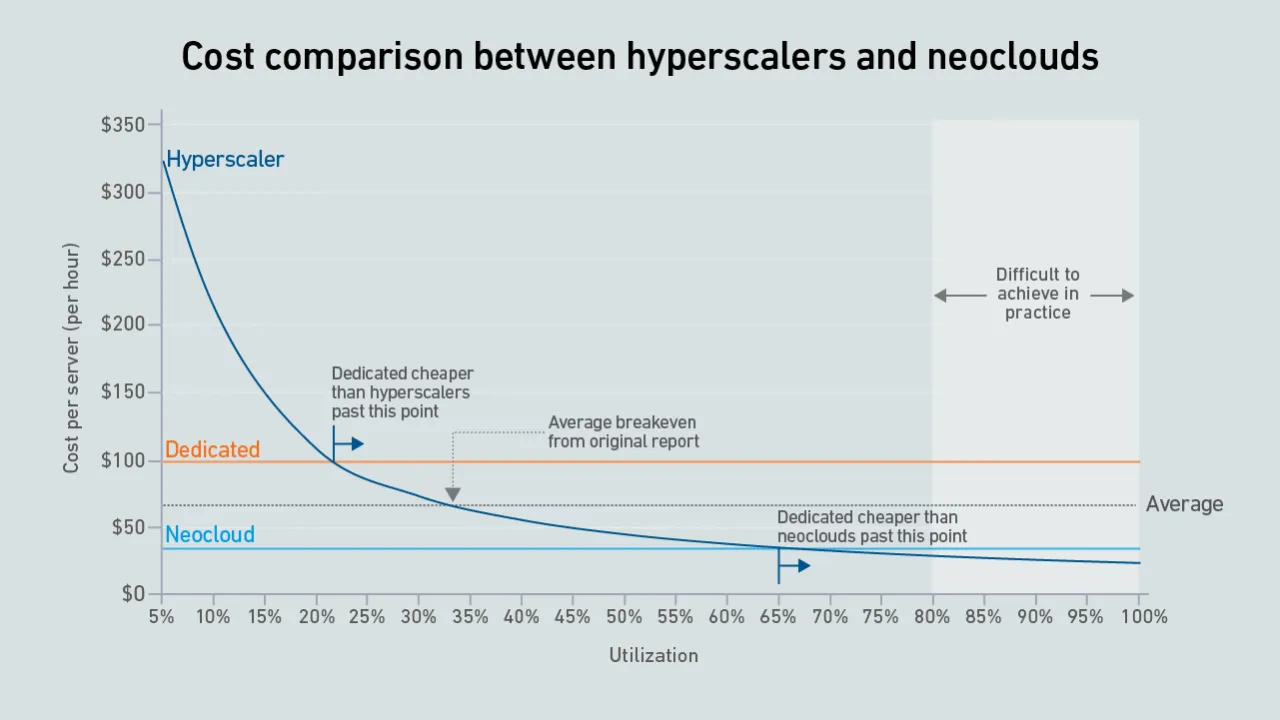
A new wave of GPU-focused cloud providers is offering high-end hardware at prices lower than those charged by hyperscalers. Dedicated infrastructure needs to be highly utilized to outperform these neoclouds on cost.
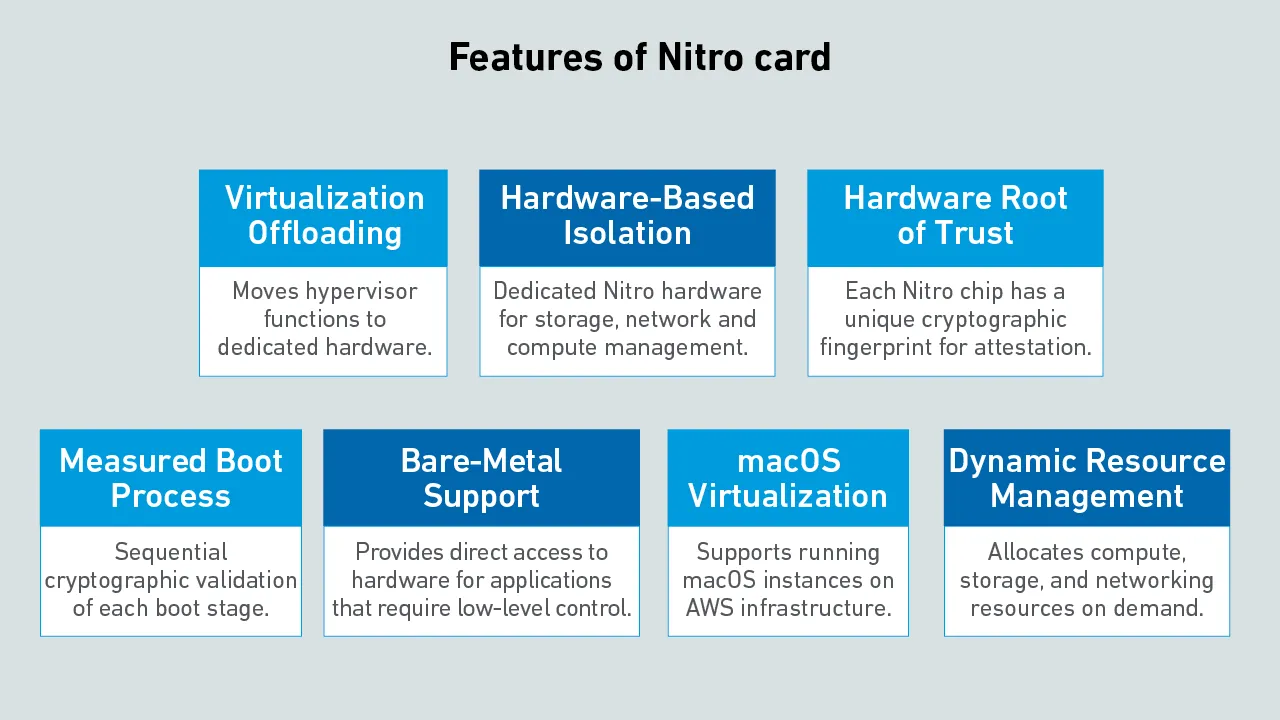
Hyperscalers design their own servers and silicon to scale colossal server estates effectively. AWS uses a system called Nitro to offload virtualization, networking and storage management from the server processor onto a custom chip.