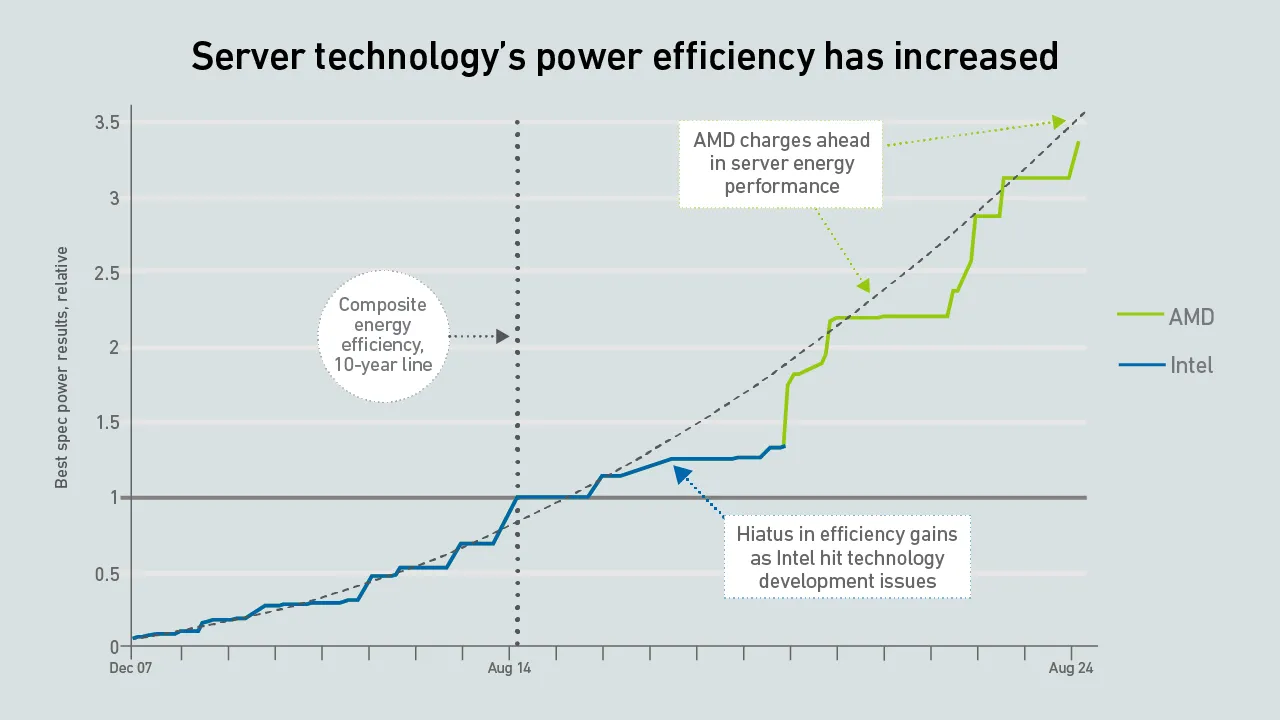
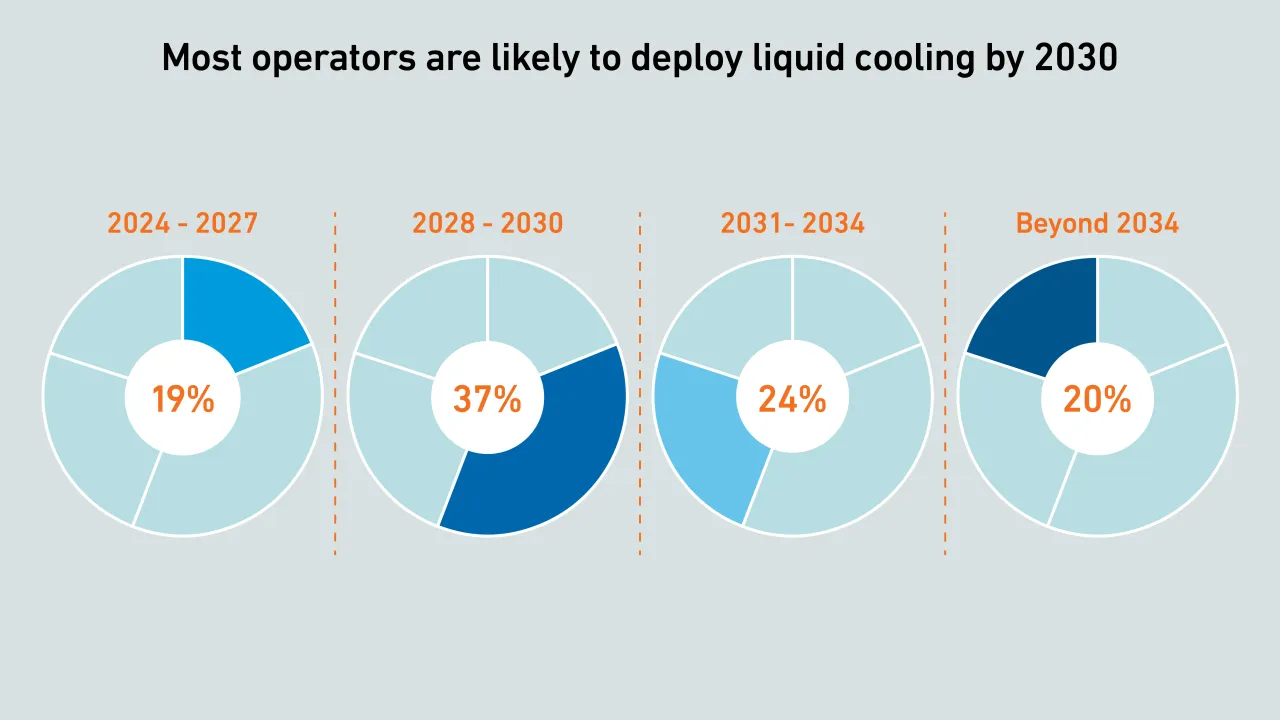
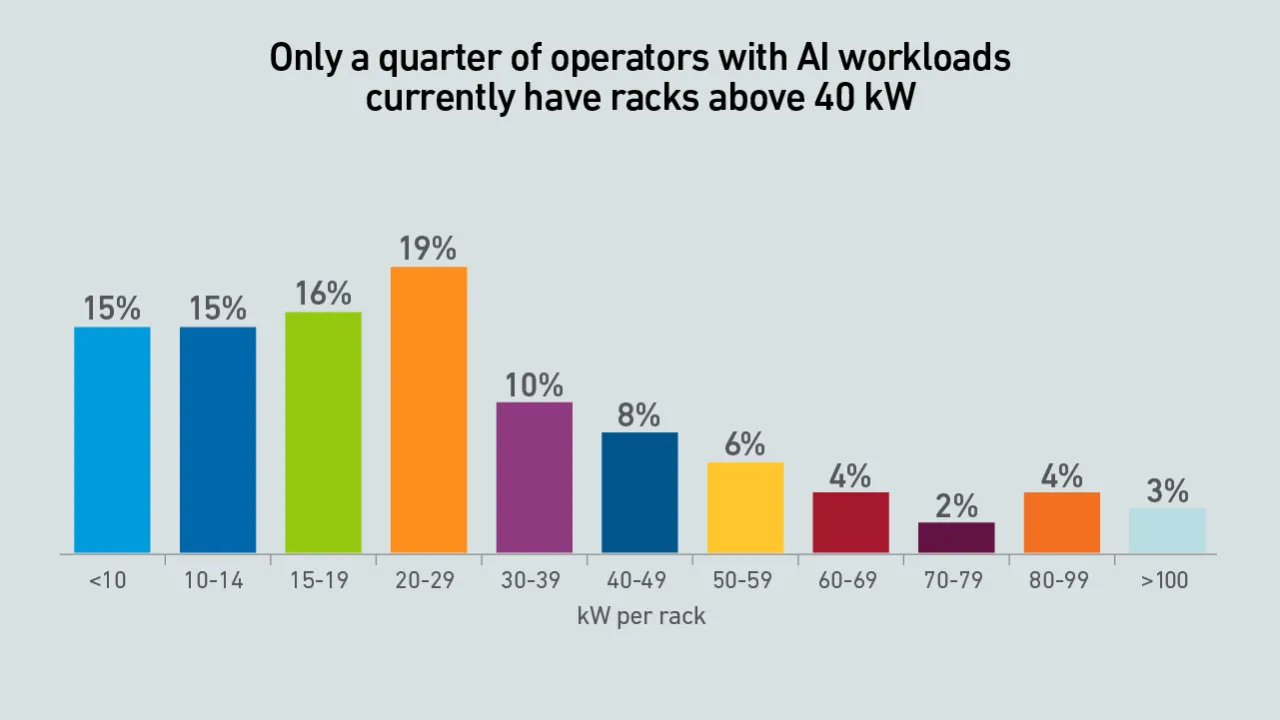
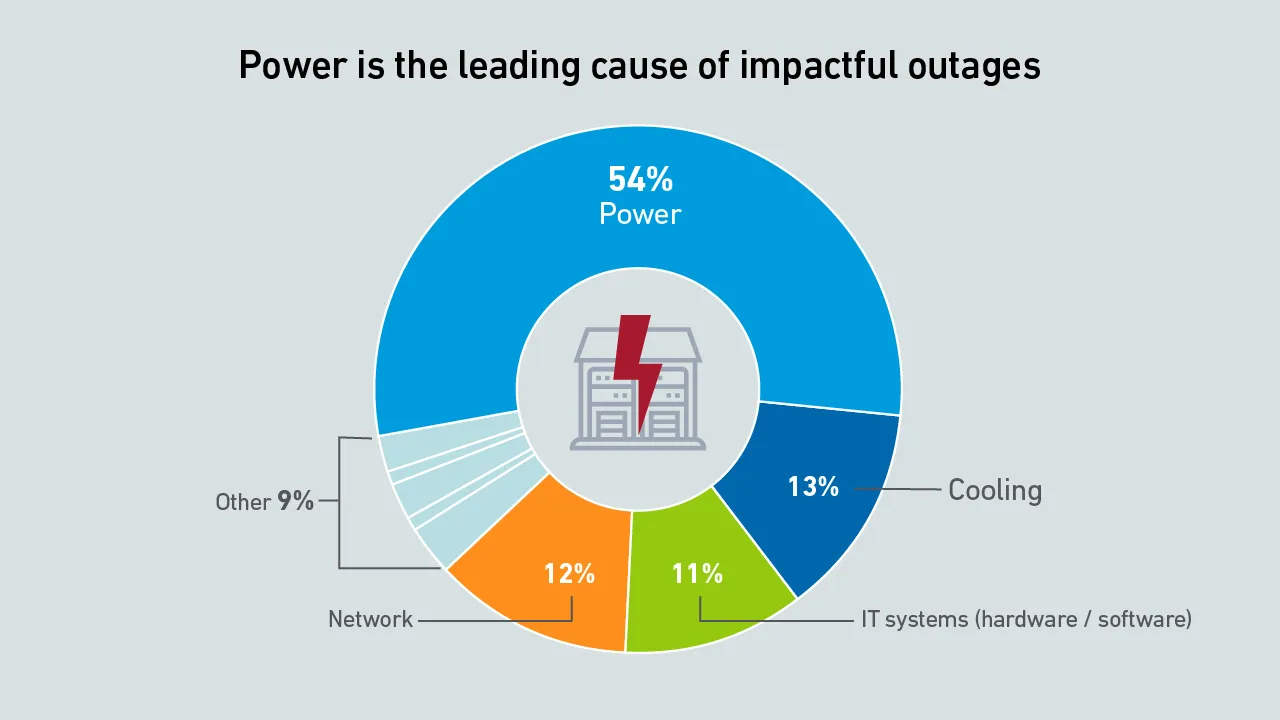
Many organizations still do not tap into the potential power efficiency gains hidden in servers. Without operational focus on extracting those, future server platforms may bring marginal, if any, energy performance improvements.

Daniel Bizo
Over the past 15 years, Daniel has covered the business and technology of enterprise IT and infrastructure in various roles, including industry analyst and advisor. His research includes sustainability, operations, and energy efficiency within the data center, on topics like emerging battery technologies, thermal operation guidelines, and processor chip technology.
dbizo@uptimeinstitute.com
Latest Research
Schneider Electric's acquisition of Motivair Corporation aims to fill product gaps and meet future demand - which will be good for customers if it helps to reduce industry fragmentation
AI training clusters can show rapid and large swings in power consumption. This behavior is likely driven by a combination of properties of both modern compute silicon and AI training software - and may be difficult to manage at scale.
Densification is - once again - high on the agenda, with runaway expectations largely due to compute power requirements of generative AI workloads. Will this time be different? Uptime's 2024 global survey of data center managers offers some clues.
Most operators will be familiar with the outrageous power and cooling demands of hardware for generative AI. Why are these systems so difficult to accommodate, and what does this mean for the future of data center design?
The data center industry's largest and most influential survey results are in! Join us as we discuss the 14th Annual Uptime Global Data Center Survey 2024 which reveals an industry that is expanding, and is also planning for major technological,…
The 14th edition of the Uptime Institute Global Data Center Survey highlights the experiences and strategies of data center owners and operators in the areas of resiliency, sustainability, efficiency, staffing, cloud and AI.
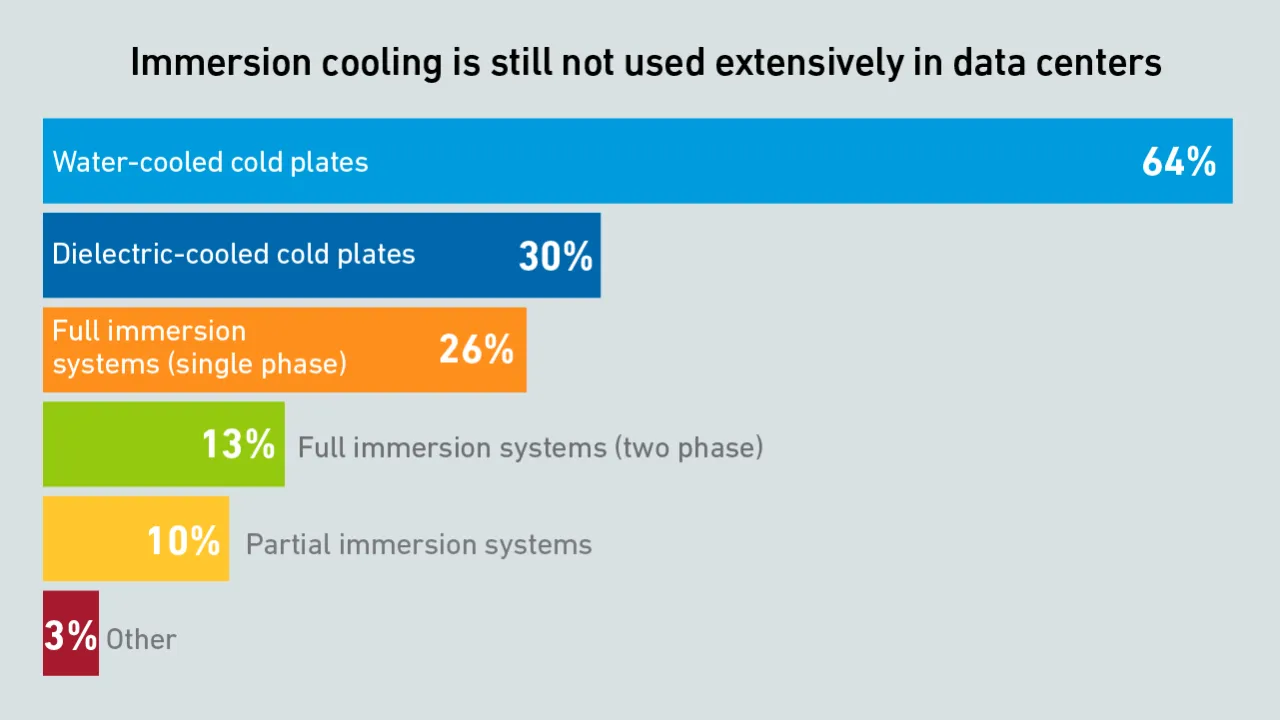
Two-phase immersion was expected to revolutionize data center cooling but proved difficult to implement. With escalating silicon thermal power, two-phase is gaining substantial interest again, just in a different form: direct-to-chip liquid cooling.
There are no commonly accepted best practices or standards to refer to when assessing the fire hazard that single-phase immersion fluids pose in a data center application and the appropriate measures against them.
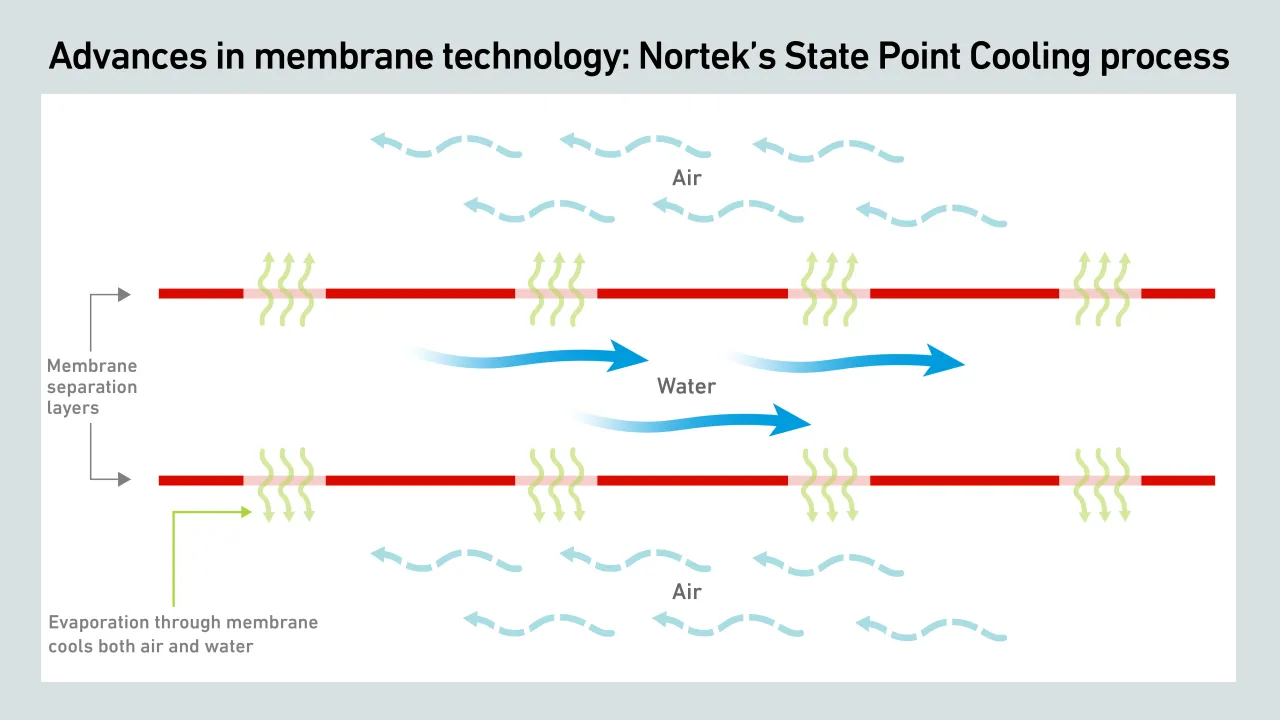
This report discusses recent innovations in air cooling, such as advanced evaporative cooling methods, AI-driven facility management and cutting-edge server heat sinks.
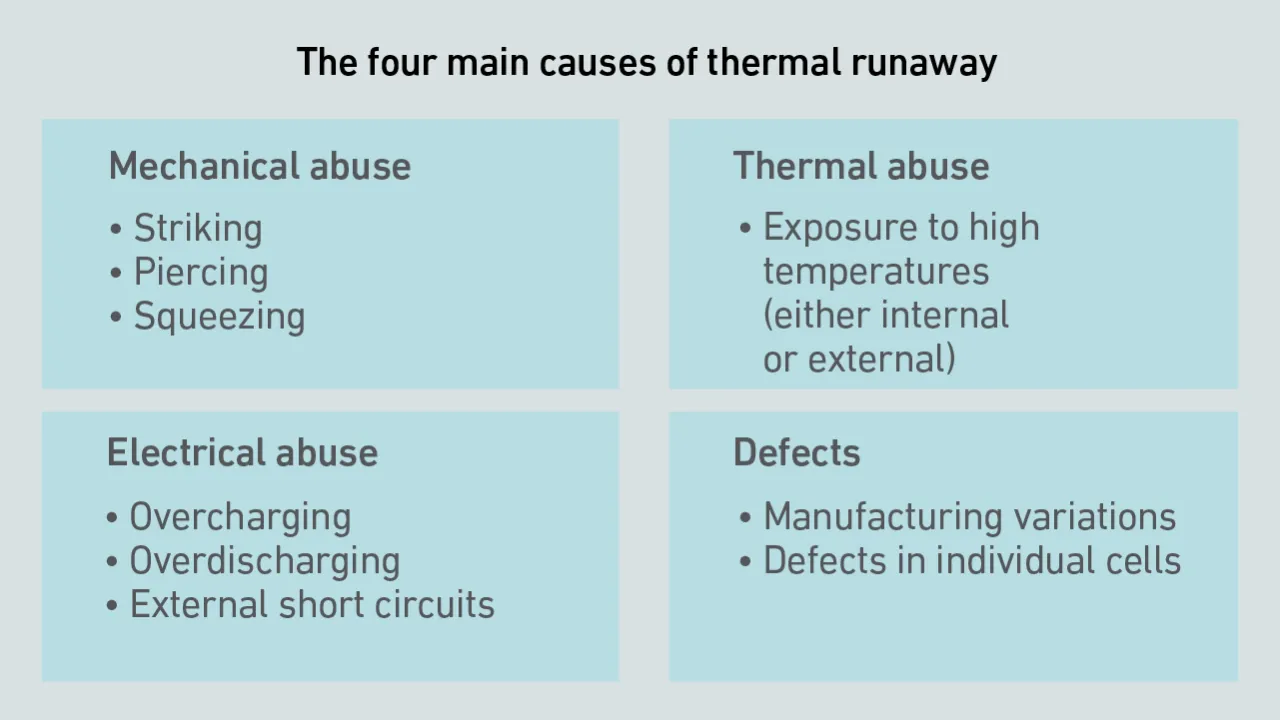
While the fire risk with lithium-ion batteries is widely understood, guidance on how best to mitigate it is still evolving. Controlling a Li-ion fire is difficult because of chemistry that creates the risk of thermal runaway.
This report outlines the characteristics of machine learning (ML) applications, describes production use cases for ML-based software in data center M&O, and profiles several vendors offering AI-based functionality in their products.
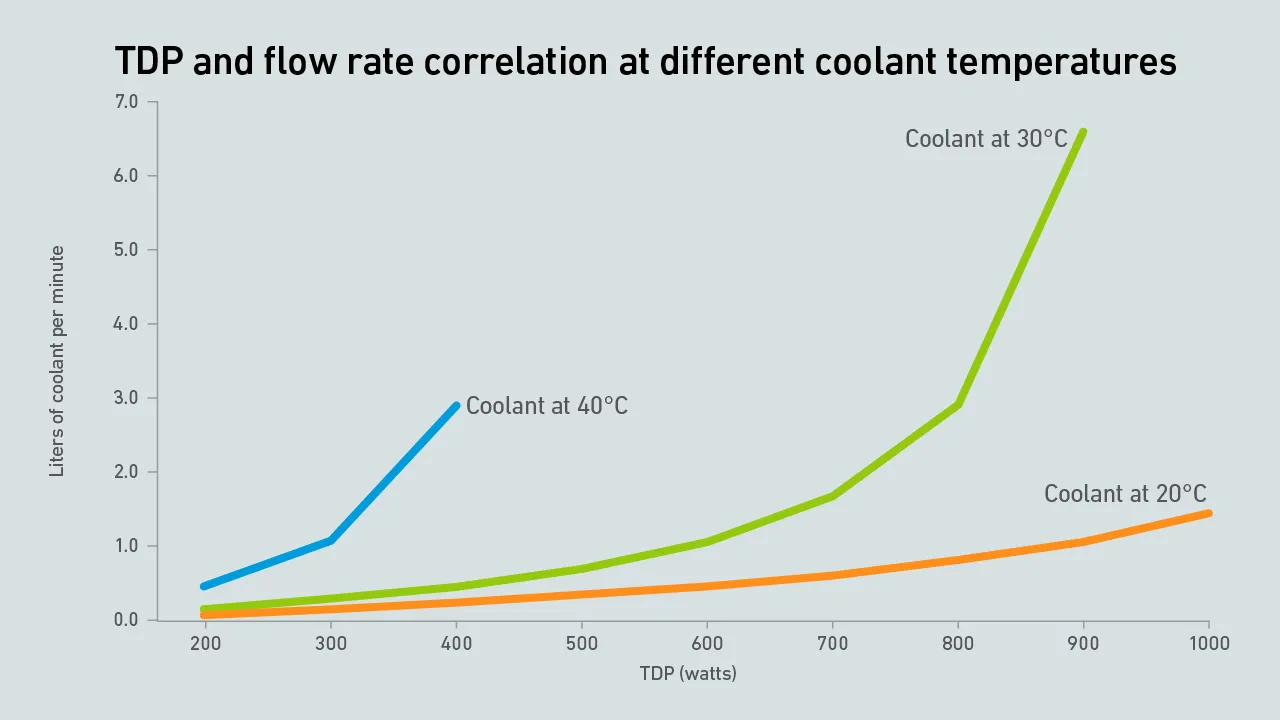
It is becoming a near certainty that many facility operators will use direct liquid cooling within a few years. This raises a number of engineering questions, one of which is how to size coolant distribution units.
Refrigeration's history of progress is also a history of environmental concern. Whenever new refrigerants solve a problem, they create further crises down the line - and now history appears to be repeating itself.
Preliminary calculations by Uptime Intelligence suggest the initial impact of generative AI on global data center power use is low - but it will rise quickly as adoption increases. How far generative AI will go remains unclear.