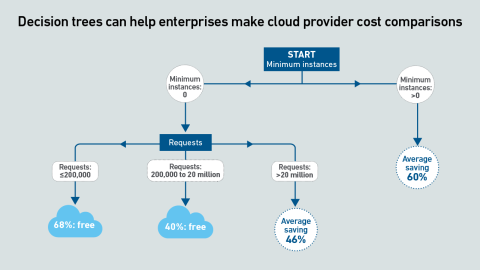
Serverless container services enable rapid, per-second scalability, which is ideal for AI inference. However, inconsistent and opaque pricing metrics hinder comparisons. This pricing tool compares the cost of services across providers.
filters
Explore All Topics
Serverless container services enable rapid scalability, which is ideal for AI inference. However, inconsistent and opaque pricing metrics hinder comparisons. This report uses machine learning to derive clear guidance by means of decision trees.
Current geopolitical tensions are eroding some European organizations’ confidence in the security of hyperscalers; however, moving away from them entirely is not practically feasible.
Training large transformer models is different from all other workloads — data center operators need to reconsider their approach to both capacity planning and safety margins across their infrastructure.
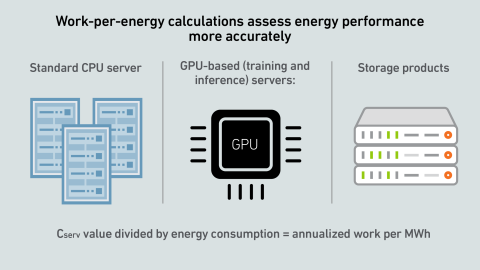
A report by Uptime's Sustainability and Energy Research Director Jay Dietrich merits close attention; it outlines a way to calculate data center IT work relative to energy consumption. The work is supported by Uptime Institute and The Green Grid.
Today, GPU designers pursue outright performance over power efficiency. This is a challenge for inference workloads that prize efficient token generation. GPU power management features can help, but require more attention.
The 15th edition of the Uptime Institute Global Data Center Survey highlights the experiences and strategies of data center owners and operators in the areas of resiliency, sustainability, efficiency, staffing, cloud and AI. The attached data files…
As AI workloads surge, managing cloud costs is becoming more vital than ever, requiring organizations to balance scalability with cost control. This is crucial to prevent runaway spend and ensure AI projects remain viable and profitable.
The US government’s AI compute diffusion rules, introduced in January 2025, will be rescinded — with new rules coming. It warns any dealings linked to advanced Chinese chips will require US export authorization. Operators still face tough demands.
Many operators expect GPUs to be highly utilized, but examples of real-world deployments paint a different picture. Why are expensive compute resources being wasted — and what effect does this have on data center power consumption?
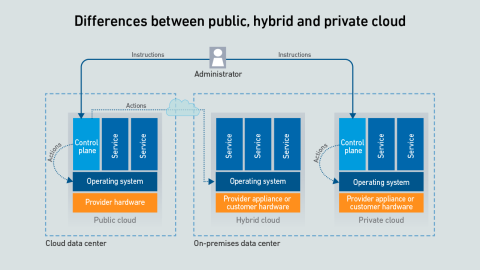
Hyperscalers offer a confusing array of on-premises versions of their public cloud-enabling infrastructure — the differences between them are rooted in whether the customer or the provider manages the control plane and server hardware.
AI vendors claim that “reasoning” can improve the accuracy and quality of the responses generated by LLMs, but this comes at a high cost. What does this mean for digital infrastructure?
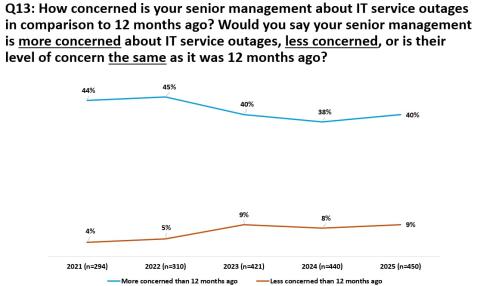
Results from Uptime Institute's 2025 Data Center Resiliency Survey (n=970) focus on data center resiliency issues and the impact of outages on the data center sector globally.The attached data files below provide full results of the survey,…
High-end AI systems receive the bulk of the industry’s attention, but organizations looking for the best training infrastructure implementation have choices. Getting it right, however, may take a concerted effort.
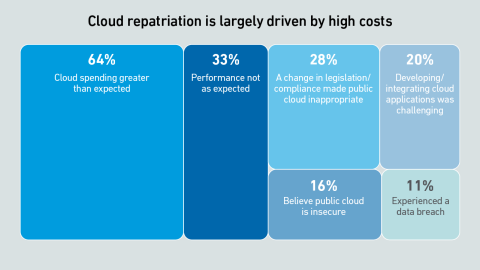
Scalability and cost efficiency are the top reasons enterprises migrate to the cloud, but scalability issues due to application design flaws can lead to spiralling costs — and some workload repatriation to on-premises facilities
 Dr. Owen Rogers
Dr. Owen Rogers


 Daniel Bizo
Daniel Bizo
 Andy Lawrence
Andy Lawrence
 Max Smolaks
Max Smolaks
 Paul Carton
Paul Carton
 Anthony Sbarra
Anthony Sbarra
 Laurie Williams
Laurie Williams



 Douglas Donnellan
Douglas Donnellan