Preliminary calculations by Uptime Intelligence suggest the initial impact of generative AI on global data center power use is low - but it will rise quickly as adoption increases. How far generative AI will go remains unclear.
filters
Explore All Topics
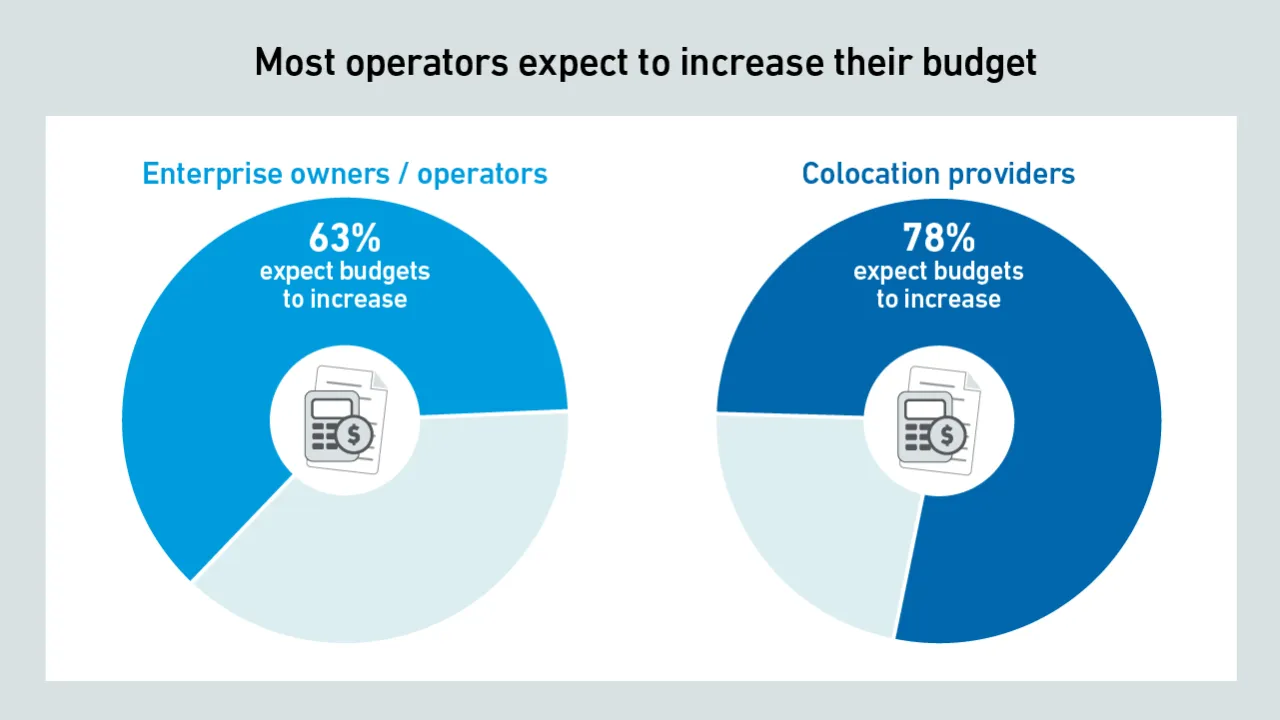
Data center budgets are expected to increase in 2024 for most organizations, but ongoing supply chain issues and staffing challenges may restrict investments, according to recent Uptime Intelligence survey data.
Large colocation and public cloud companies have been growing strongly and very publicly, but enterprises continue to add data center capacity too, Uptime Intelligence data shows.
This session describes the questions organizations need to answer around technology roadmaps, market growth and workload requirements to effectively plan the data center builds of the near future.
Unpredictable costs and "bill shocks" are a growing problem for organizations running their applications and workloads in the public cloud. FinOps could help enterprises analyze, report and optimize cloud and other IT costs.
Recent publication of the EU Energy Efficiency Directive Task B and C reports clarify most of the data reporting requirements and set out the preferred policy options for assessing data center energy performance.
The data center industry's largest and most influential survey results are in! Join us as we discuss the 13th Annual Uptime Global Data Center Survey 2023 which reveals an industry that is growing, dynamic and increasingly resilient.
Uptime Intelligence has been providing regular updates and insights on the efforts of the European Parliament and European Commission (EC) to finalize the Energy Efficiency Directive (EED) recast requirements. The directive is the most radical and…
75% of organizations in North America have experienced supply chain delays. With organizations already stretching equipment life-cycles, how do we stay ahead of equipment and spare shortages that could leave us vulnerable?
The public cloud’s on-demand pricing model is vital in enabling application scalability — the key benefit of cloud computing. Resources need to be readily available for a cloud application to scale when required without the customer having to give…
Operators report that their sustainability initiatives not only benefit the environment - they also reduce operating costs and improve customer engagement. Sustainability strategies, however, vary widely.
There is evidence that outage rates have been gradually falling in recent years. This report brings together and analyzes recent Uptime Institute data on IT and data center outage trends: their causes, costs and consequences.
Hyperscale cloud providers have opened numerous operating regions in all corners of the world over the past decade. The three most prominent — Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure — now have 105 distinct regions (excluding…
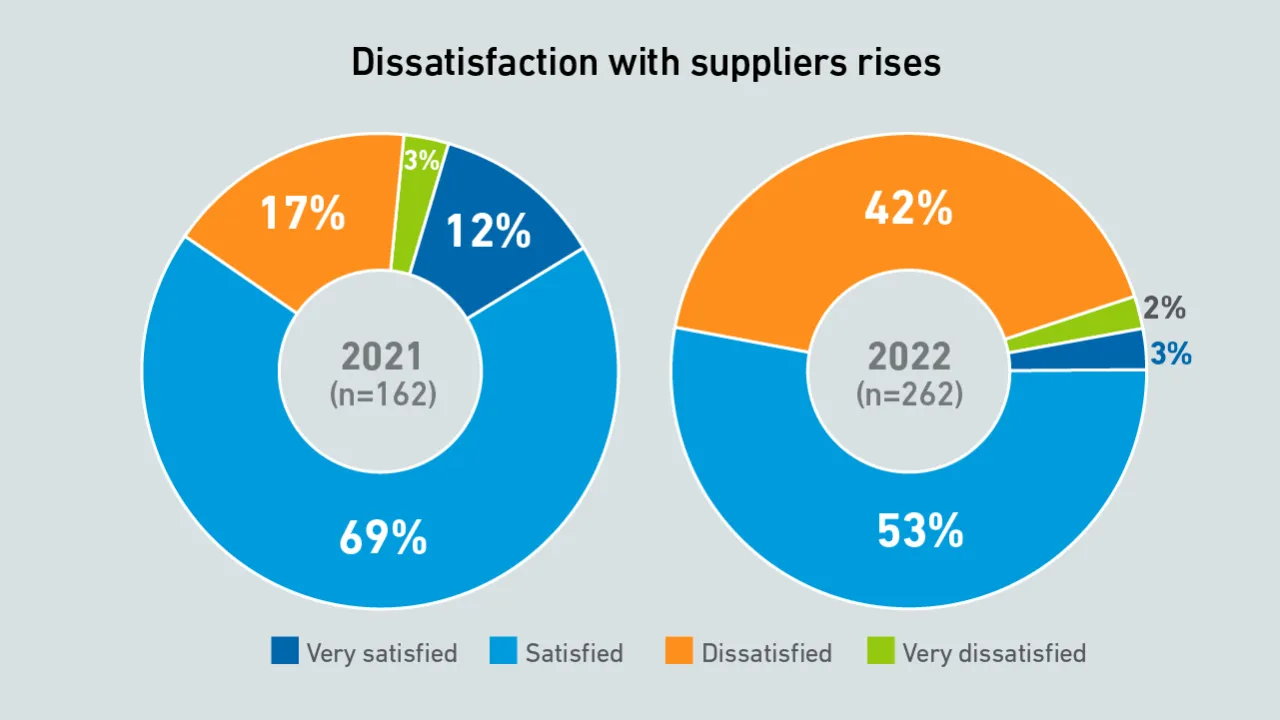
Uptime Intelligence finds that operators and vendors face major delays in the supply of equipment, and are increasingly dissatisfied with their suppliers.
The past decade has seen numerous reports of so-called cloud “repatriations” — the migration of applications back to on-premises venues following negative experiences with, or unsuccessful migrations to, the public cloud.A recent Uptime Update (High…
 Andy Lawrence
Andy Lawrence
 Daniel Bizo
Daniel Bizo
 Douglas Donnellan
Douglas Donnellan
 Todd Traver
Todd Traver
 Antonio Piraino
Antonio Piraino

 John O'Brien
John O'Brien
 Jay Dietrich
Jay Dietrich
 Chris Brown
Chris Brown
 Jacqueline Davis
Jacqueline Davis
 Matt Stansberry
Matt Stansberry

 Dr. Owen Rogers
Dr. Owen Rogers

 Lenny Simon
Lenny Simon