Uptime Intelligence looks beyond the more obvious trends of 2025 and examines some of the latest developments and challenges shaping the data center industry.
filters
Explore All Topics
Supersized generative AI models are placing onerous demands on both IT and facilities infrastructure. The challenge for next-generation AI infrastructure will be power, forcing operators to explore new electrification architectures.
Nvidia's dominant position in the AI hardware market may be steering data center design in the wrong direction. This dominance will be harder to sustain as enterprises begin to understand AI and opt for cheaper, simpler hardware.
The cost and complexity of deploying large-scale GPU clusters for generative AI training will drive many enterprises to the public cloud. Most enterprises will use pre-trained foundation models, to reduce computational overheads.
Enterprises have much enthusiasm for AI, interviews and workshops by Uptime Intelligence suggest, but this is tempered by caution. Most hope to avoid disruptive, expensive or careless investments.
Enterprises have various options on how and where to deploy their AI training and inference workloads. This report explains how these different options balance cost, complexity and customization.
While GPUs are the power-hungry devices that enable effective AI training, it is innovations in software that are fueling the recent surge in interest and investment. This report explains how neural networks power generative AI.
AI training clusters can show rapid and large swings in power consumption. This behavior is likely driven by a combination of properties of both modern compute silicon and AI training software - and may be difficult to manage at scale.
Generative AI models brought about an influx of high-density cabinets. There has been much focus on how to best manage thermal issues, but the weight of power distribution equipment is a potentially overlooked concern.
Most operators will be familiar with the outrageous power and cooling demands of hardware for generative AI. Why are these systems so difficult to accommodate, and what does this mean for the future of data center design?
The 14th edition of the Uptime Institute Global Data Center Survey highlights the experiences and strategies of data center owners and operators in the areas of resiliency, sustainability, efficiency, staffing, cloud and AI.
Although there is still uncertainty around the rate of AI adoption, many organizations are pushing ahead to avoid being left behind. However, behind this enthusiasm, there are six issues that operators face when hosting AI.
Preliminary calculations by Uptime Intelligence suggest the initial impact of generative AI on global data center power use is low - but it will rise quickly as adoption increases. How far generative AI will go remains unclear.
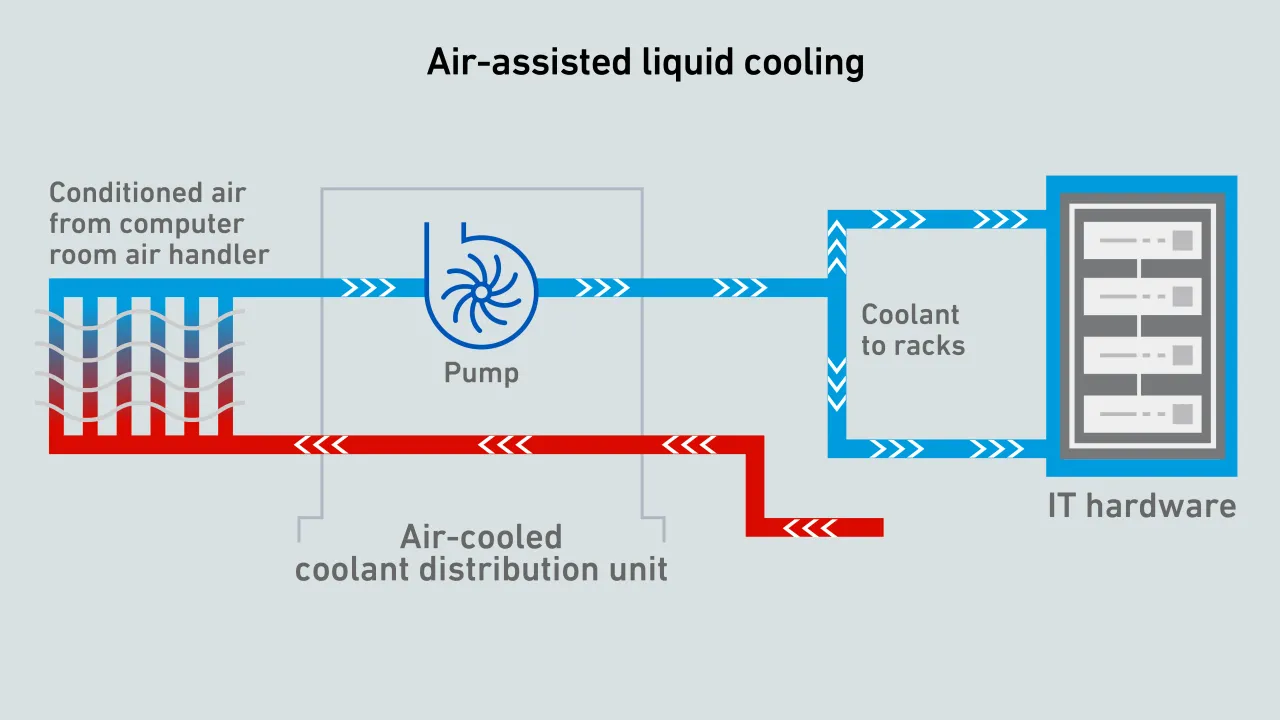
Air-assisted direct liquid cooling systems offer trade-offs that make them attractive to operators looking to address server cooling and rack density challenges - and are relatively easy to install and maintain.
Uptime Intelligence looks beyond the more obvious trends of 2024 and identifies some challenging issues. Strong IT demand, high-density IT systems and tough sustainability requirements will drive a new wave of investment.
 Andy Lawrence
Andy Lawrence
 Daniel Bizo
Daniel Bizo
 Douglas Donnellan
Douglas Donnellan
 Max Smolaks
Max Smolaks
 Peter Judge
Peter Judge
 Dr. Owen Rogers
Dr. Owen Rogers





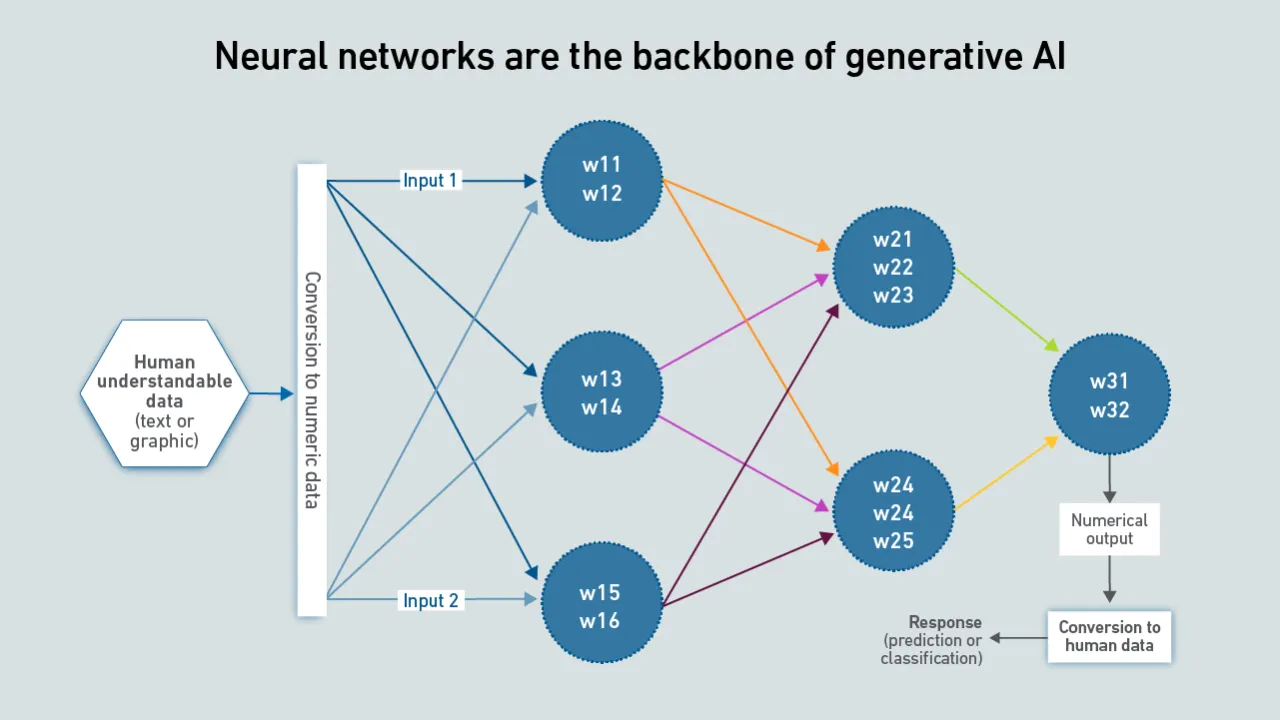



 John O'Brien
John O'Brien
 Jacqueline Davis
Jacqueline Davis
 Jabari Williams-George
Jabari Williams-George
 Rose Weinschenk
Rose Weinschenk