Many operators expect GPUs to be highly utilized, but examples of real-world deployments paint a different picture. Why are expensive compute resources being wasted - and what effect does this have on data center power consumption?
filters
Explore All Topics
Digital twins are increasingly valued in complex data center applications, such as designing and managing facilities for AI infrastructure. Digitally testing and simulating scenarios can reduce risk and cost, but many challenges remain.
While AI infrastructure build-out may focus on performance today, over time data center operators will need to address efficiency and sustainability concerns.
High-end AI systems receive the bulk of the industry's attention, but organizations looking for the best training infrastructure implementation have choices. Getting it right, however, may take a concerted effort.
The high capital and operating costs of infrastructure for AI mean an outage can have a significant financial impact due to lost training hours
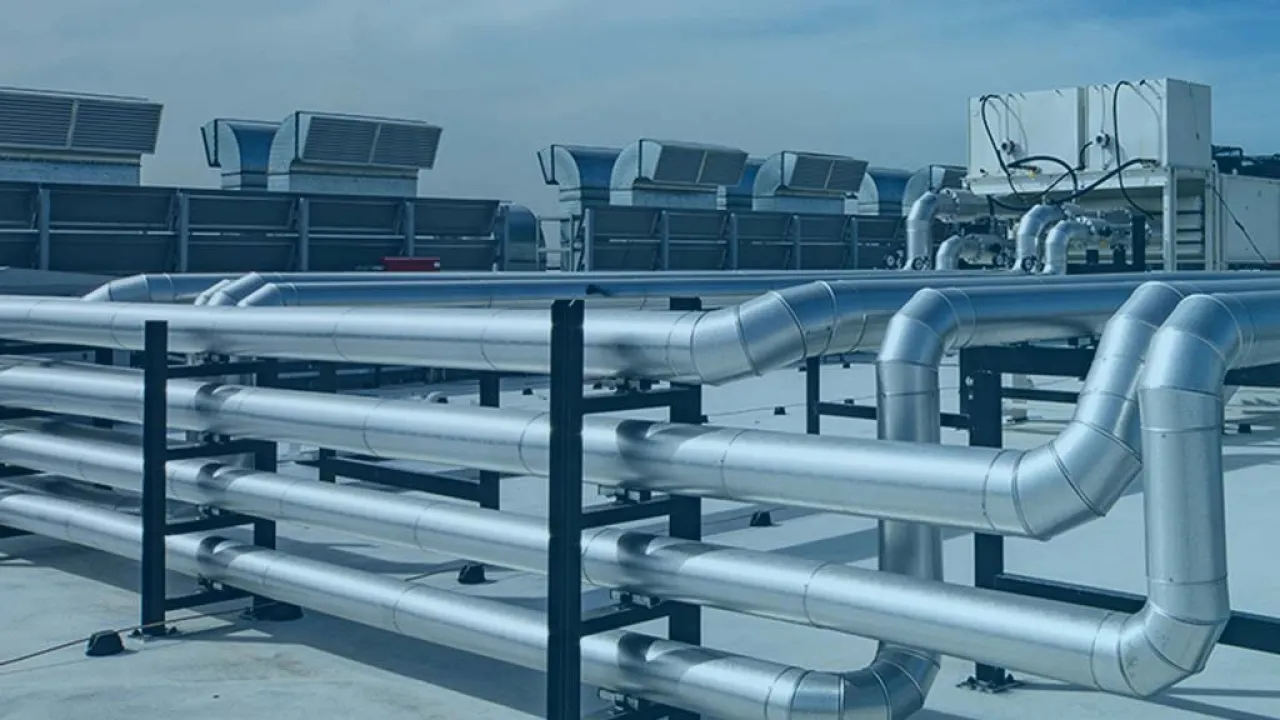
Compared with most traditional data centers, those hosting large AI training workloads require increased attention to dynamic thermal management, including capabilities to handle sudden and substantial load variations effectively.
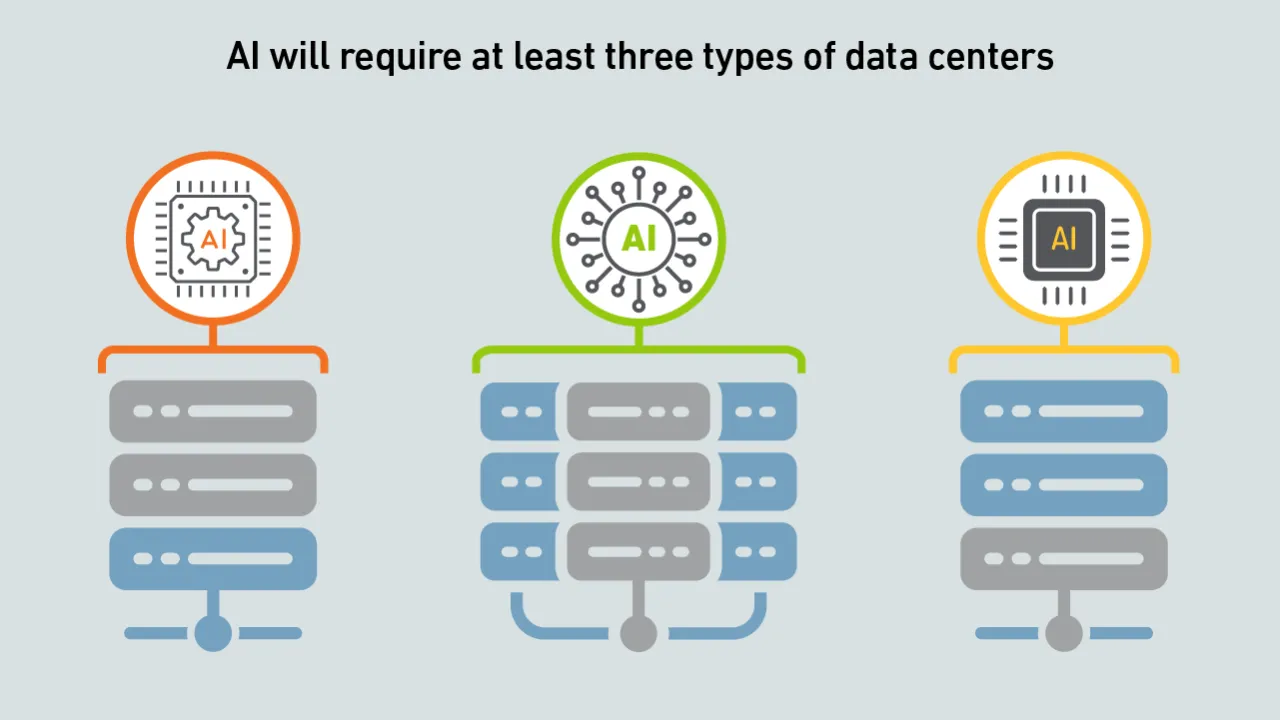
AI is not a uniform workload - the infrastructure requirements for a particular model depend on a multitude of factors. Systems and silicon designers envision at least three approaches to developing and delivering AI.
Operators and investors are planning to spend hundreds of billions of dollars on supersized sites and vast supporting infrastructures. However, increasing constraints and uncertainties will limit the scale of these build outs.
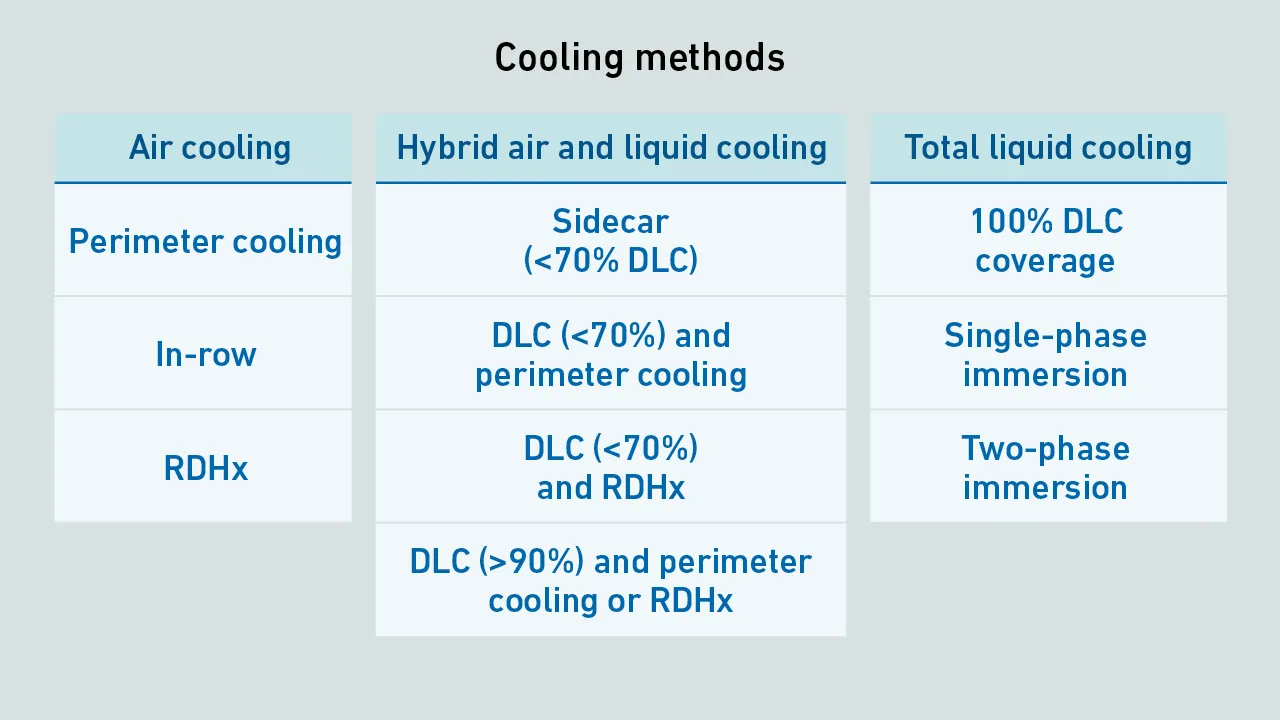
AI infrastructure increases rack power, requiring operators to upgrade IT cooling. While some (typically with rack power up to 50 kW) rely on close-coupled air cooling, others with more demanding AI workloads are adopting hybrid air and DLC.
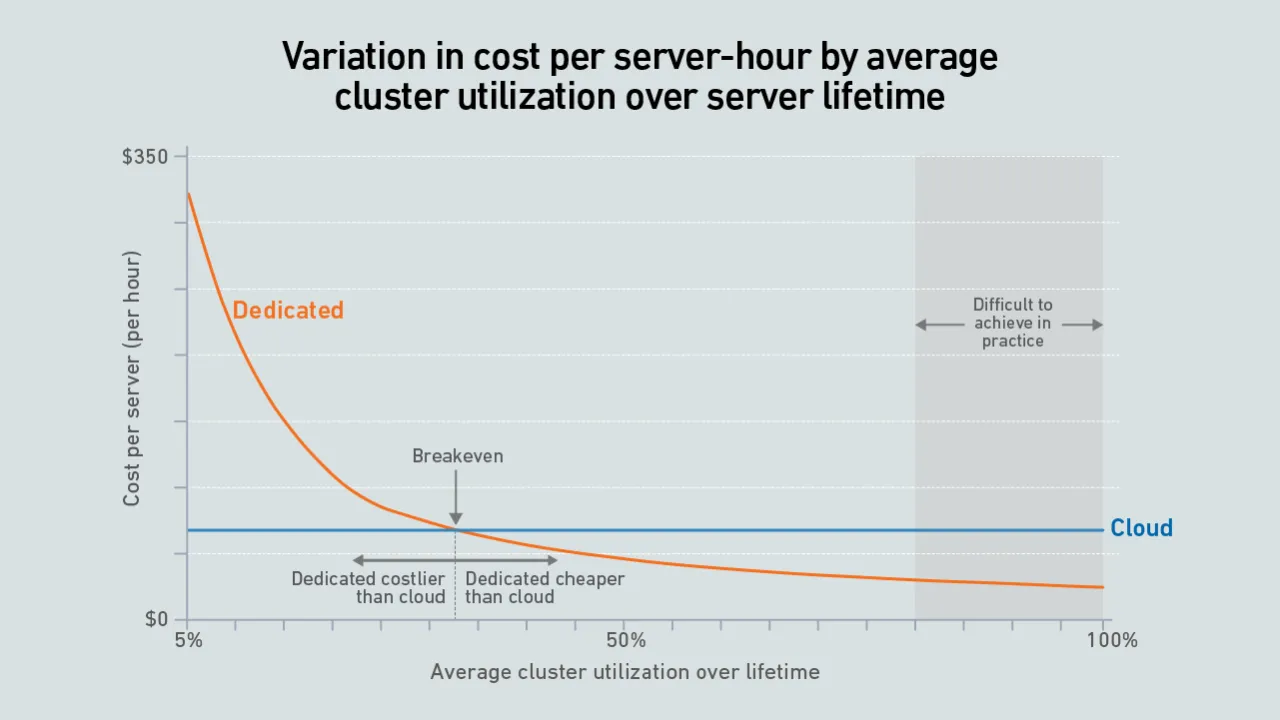
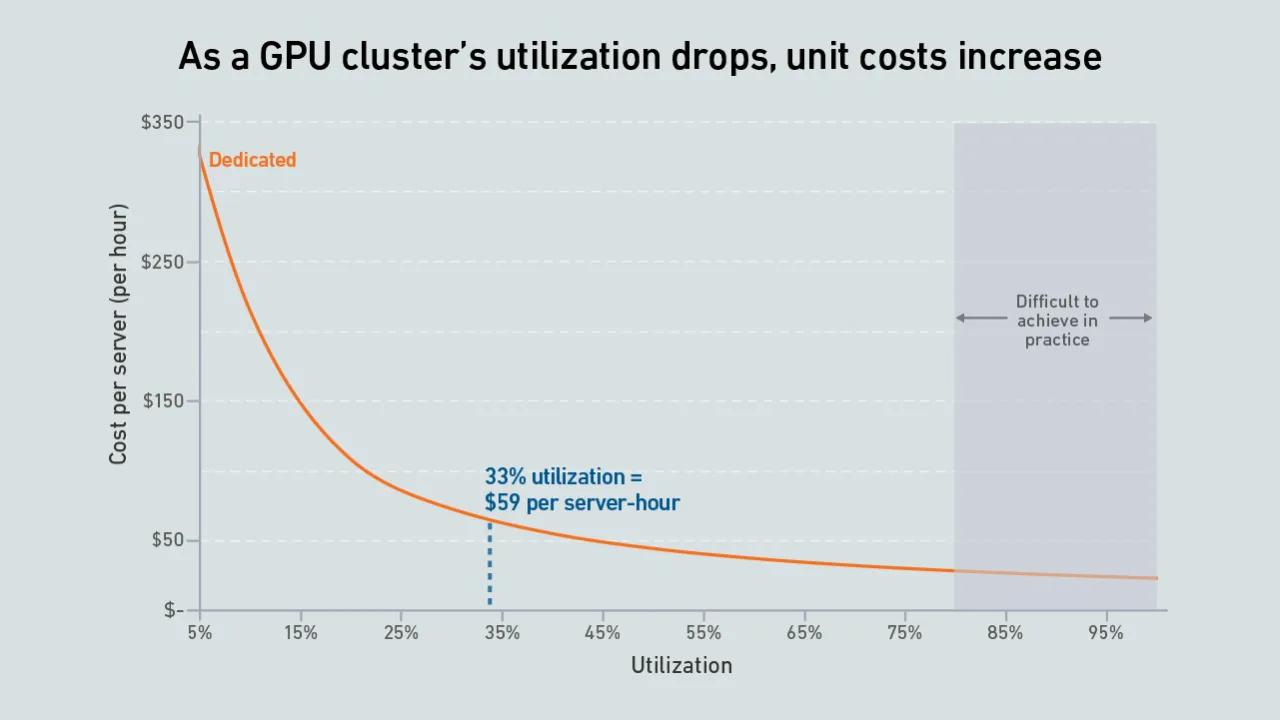
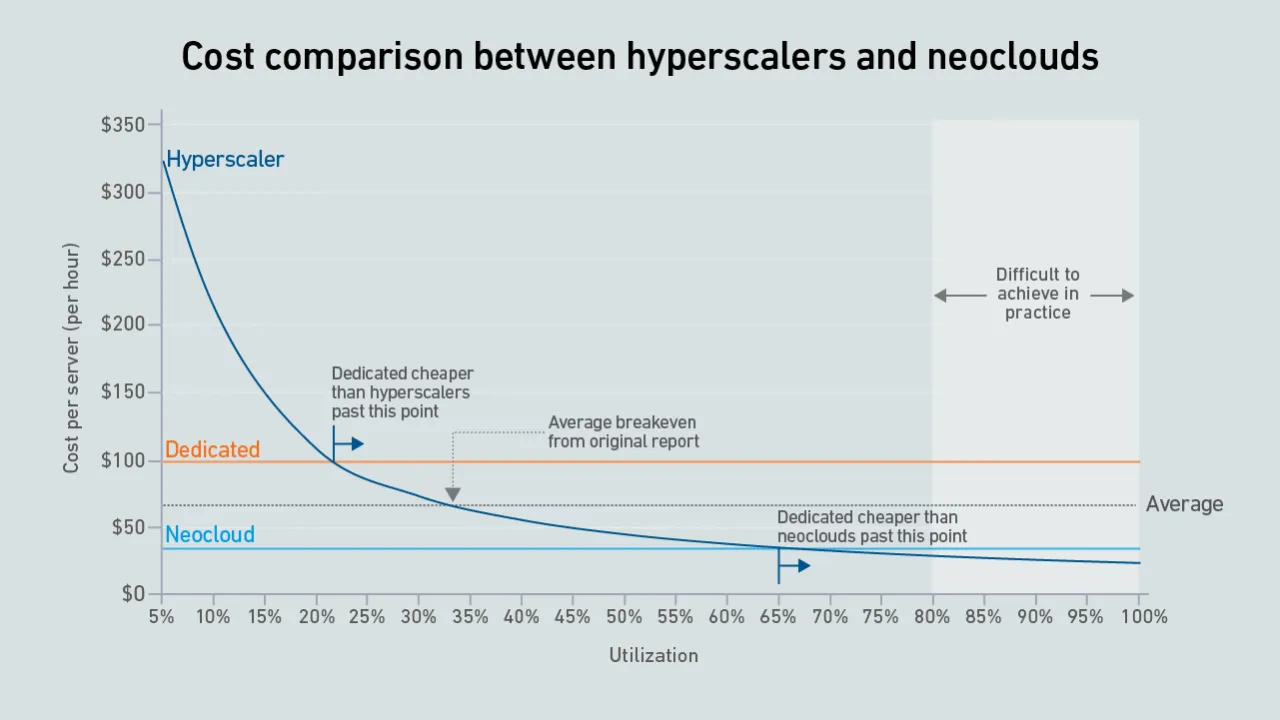
A new wave of GPU-focused cloud providers is offering high-end hardware at prices lower than those charged by hyperscalers. Dedicated infrastructure needs to be highly utilized to outperform these neoclouds on cost.
The US government is applying a new set of rules to control the building of large AI clusters around the world. The application of these rules will be complex.
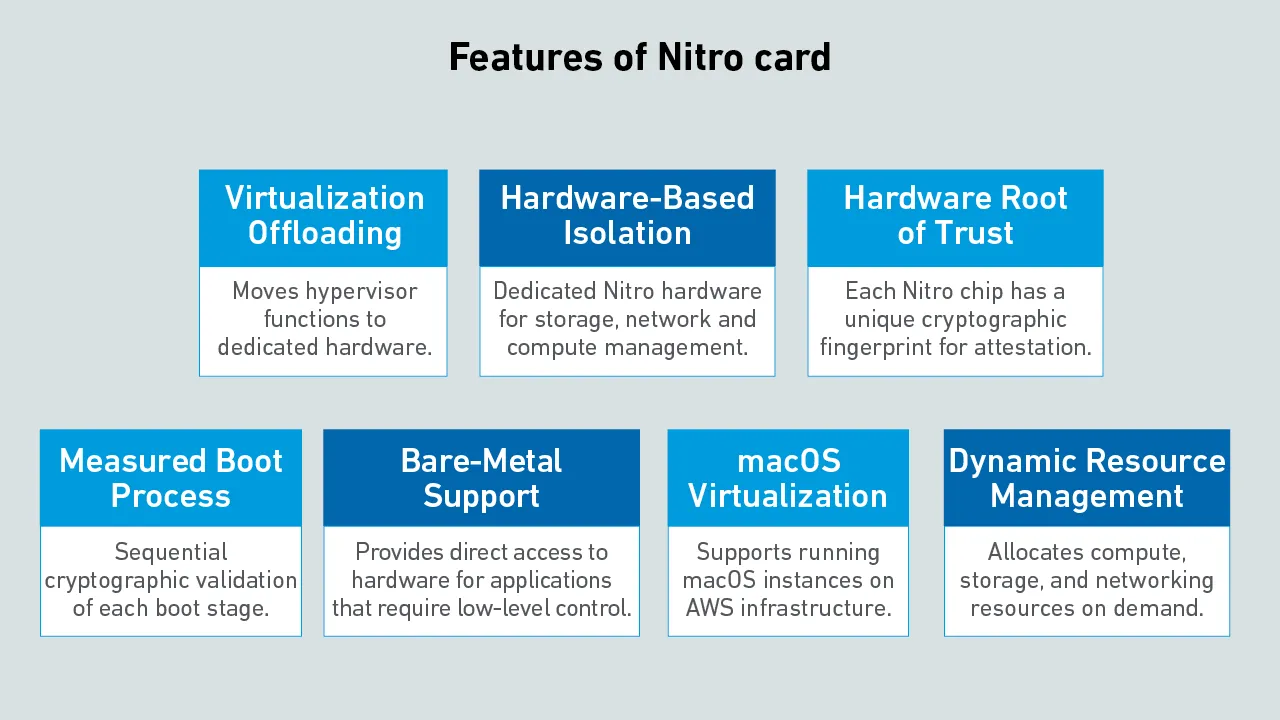
Hyperscalers design their own servers and silicon to scale colossal server estates effectively. AWS uses a system called Nitro to offload virtualization, networking and storage management from the server processor onto a custom chip.
This summary of the 2025 predictions highlights the growing concerns and opportunities around AI for data centers.
Power and cooling requirements for generative AI training are upending data center design and accelerating liquid cooling adoption. Mainstream business IT will not follow until resiliency and operational concerns are addressed.
Dedicated GPU infrastructure can beat the public cloud on cost. Companies considering purchasing an AI cluster need to consider utilization as the key variable in their calculations.
 Max Smolaks
Max Smolaks
 John O'Brien
John O'Brien
 Dr. Tomas Rahkonen
Dr. Tomas Rahkonen

 Daniel Bizo
Daniel Bizo

 Dr. Owen Rogers
Dr. Owen Rogers


 Peter Judge
Peter Judge
 Douglas Donnellan
Douglas Donnellan
 Jacqueline Davis
Jacqueline Davis