In 2026, enterprises will be more realistic about their use of generative AI, prioritizing simple use cases that deliver clear, timely value over those more innovative projects where returns — and successful outcomes — are less assured.
filters
Explore All Topics
Investment in large-scale AI has accelerated the development of electrical equipment, which creates opportunities for data center designers and operators to rethink power architectures.
The use of on-site natural gas power generation for big data centers will strain operators’ ability to meet net-zero carbon goals. To counter this, operators will increasingly explore, promote and in some cases deploy carbon capture and storage.
Uptime Intelligence looks beyond the more obvious trends of 2026 and examines some of the latest developments and challenges shaping the data center industry.
Nvidia’s DSX proposal outlines a software-led model where digital twins, modular design and automation could shape how future gigawatt-scale AI facilities operate, even though the approach remains largely conceptual.
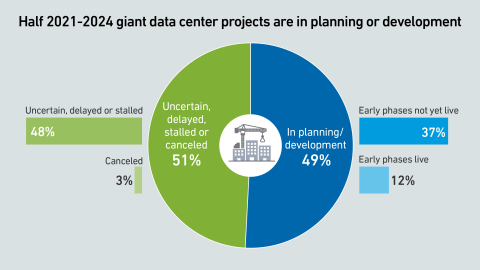
Giant data centers are being planned and built across the world to support AI, with successful projects forming the backbone of a huge expansion in capacity. But many are also uncertain, indicating risks and persistent headwinds.
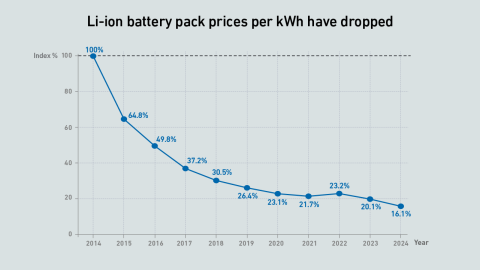
Meeting the stringent technical and commercial standards for UPS energy storage applications takes time and investment — during which Li-ion technology keeps evolving. With Natron gone, will ZincFive be able to take the opportunity?
Data4 needed to test how to build and commission liquid-cooled high-capacity racks before offering them to customers. The operator used a proof-of-concept test to develop an industrialized version, which is now in commercial operation.
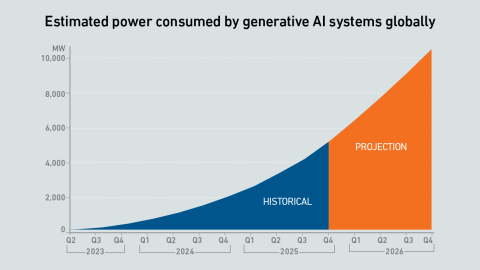
The updated model projects a doubling of power consumption by the end of 2026, with IT loads serving generative AI workloads breaking through 10 GW of capacity.
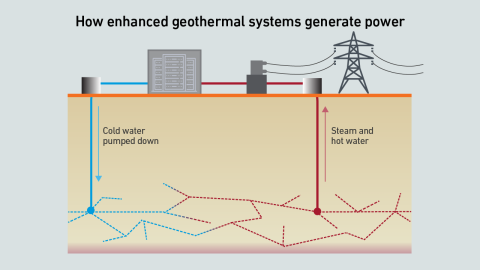
Enhanced geothermal systems use advanced drilling and hydrofracturing techniques to access geothermal energy in more locations. Some data centers may use enhanced geothermal energy for on-site, low-carbon power.
A bout of consolidation and investment activity in cooling systems in the past 12 months reflects widespread expectation of a continued spending surge on data center infrastructure.
There is an expectation that AI will be useful in data center operations. For this to happen, software vendors need to deliver new products and use cases - and these are starting to appear more often.
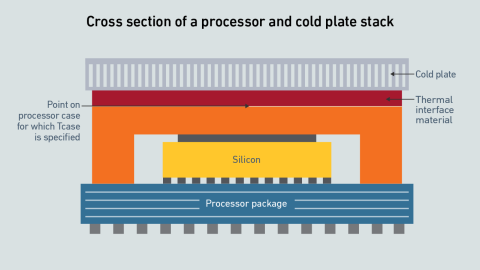
Performant cooling requires a full-system approach to eliminate thermal bottlenecks. Extreme silicon TDPs and highly efficient cooling do not have to be mutually exclusive if the data center and chip vendors work together.
Financial institutions are embracing public cloud for some mission-critical workloads, and using it as a launchpad for AI development.
Consensus is growing that a major market "correction" is coming: while some infrastructure operators are highly exposed, others may stand to benefit.
 Dr. Owen Rogers
Dr. Owen Rogers

 Daniel Bizo
Daniel Bizo

 Jay Dietrich
Jay Dietrich
 Douglas Donnellan
Douglas Donnellan
 Andy Lawrence
Andy Lawrence
 Max Smolaks
Max Smolaks
 Dr. Rand Talib
Dr. Rand Talib


 John O'Brien
John O'Brien
 Peter Judge
Peter Judge