The shortage of DRAM and NAND chips caused by demands of AI data centers is likely to last into 2027, making every server more expensive.
filters
Explore All Topics
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang's comment that liquid-cooled AI racks will need no chillers created some turbulence — however, the concept of a chiller-free data center is an old one and is unlikely to suit most operators.
Cybercriminals increasingly target supply chains as entry points for coordinated attacks; however, many vulnerabilities have been overlooked by operators and persist, despite their growing risk and severity.
Data4 needed to test how to build and commission liquid-cooled high-capacity racks before offering them to customers. The operator used a proof-of-concept test to develop an industrialized version, which is now in commercial operation.
Currently, the most straightforward way to support DLC loads in many data centers is to use existing air-cooling infrastructure combined with air-cooled CDUs.
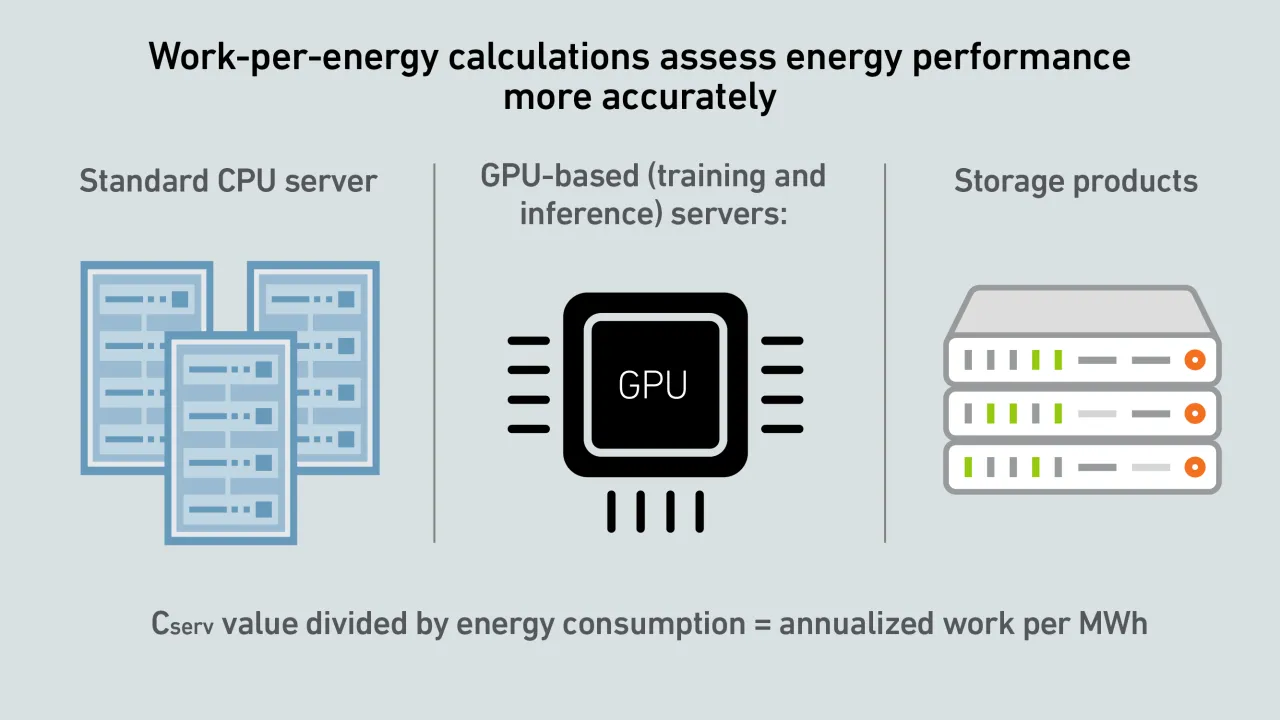
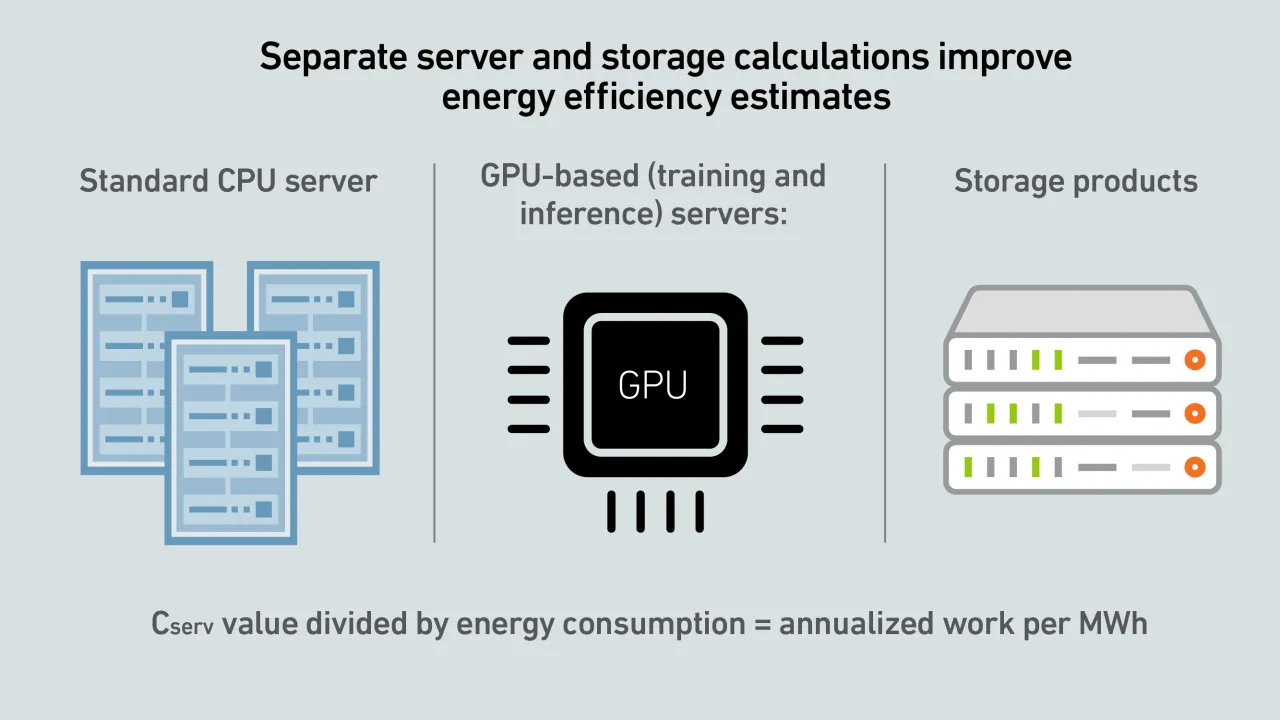
Large-scale AI training is an application of supercomputing. Supercomputing experts at the Yotta 2025 conference agree that operators need to optimize AI training efficiency and develop metrics to account for utilized power.
By raising debt, building data centers and using colos, neoclouds shield hyperscalers from the financial and technological shocks of the AI boom. They share in the upside if demand grows, but are burdened with stranded assets if it stalls.
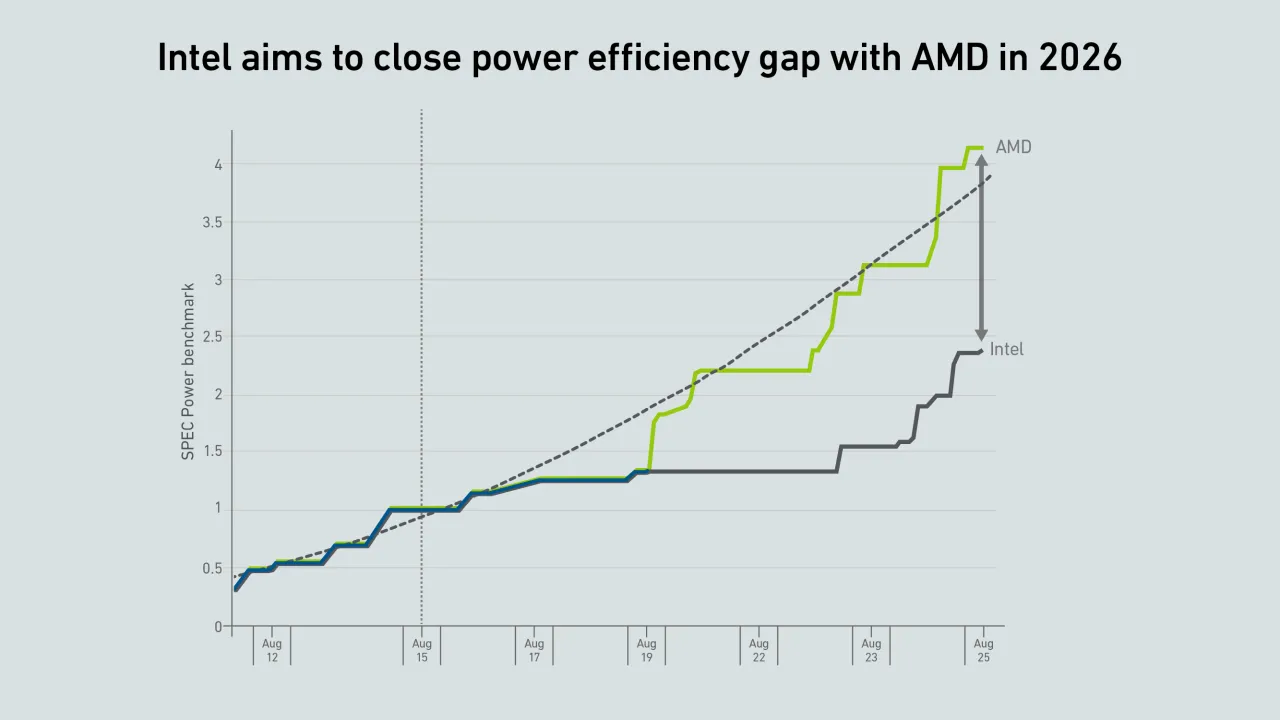
The data center industry will benefit from the race between Intel and AMD for technical supremacy, but the outlook in terms of power efficiency remains challenging.
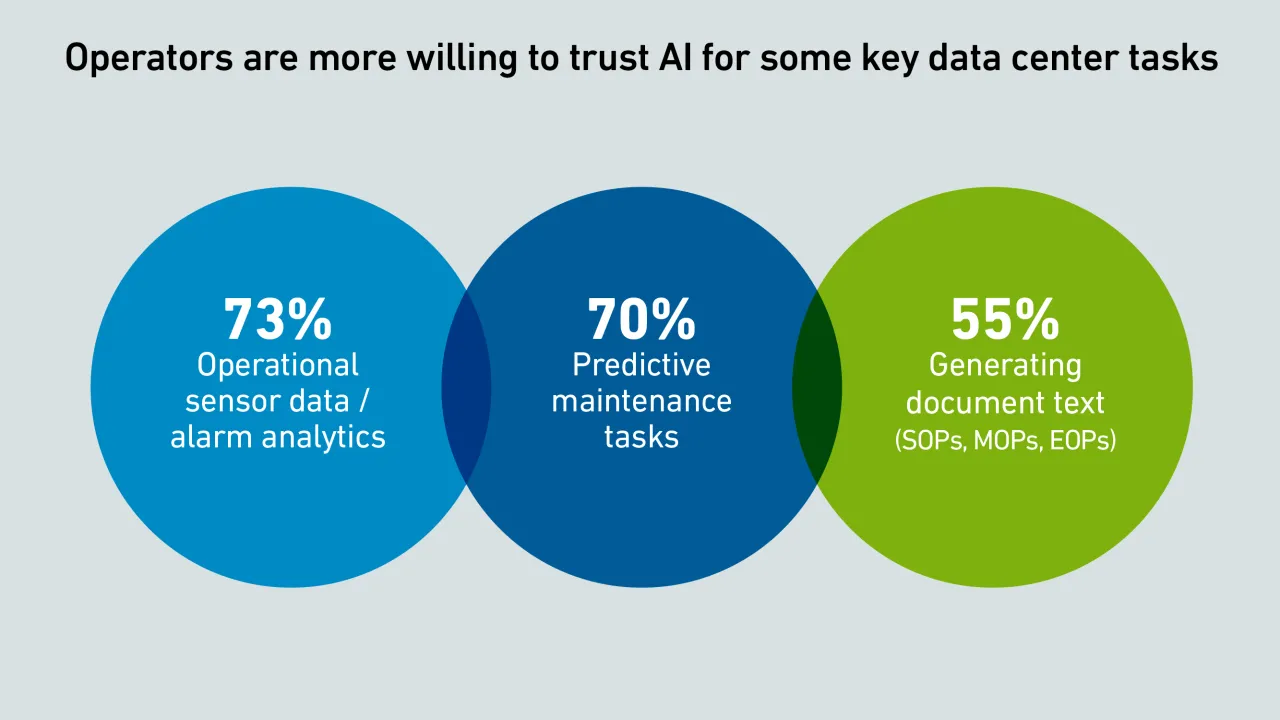
Many operators report that they trust AI to draft their MOPs, EOPs and SOPs. But this potentially error-prone approach demands meticulous review by an appropriate member of staff, or operators risk increasing the likelihood of costly downtime.
Security vulnerabilities in data center infrastructure management (DCIM) software are leaving some operators at risk of cyberattacks.
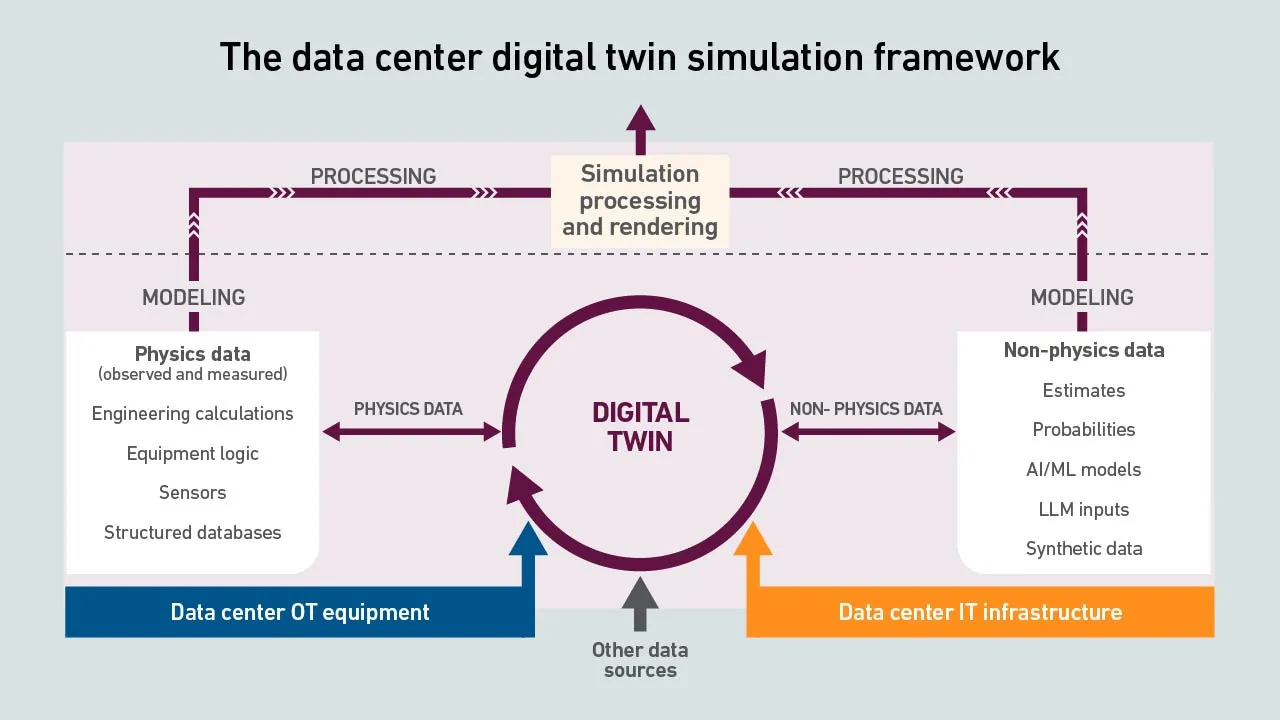
Investment in giant data centers and high-density AI infrastructure is driving a surge of interest in digital twins and AI-enabled simulations. However, experience in the field of computational fluid dynamics suggests obstacles lie ahead.
Serverless container services enable rapid, per-second scalability, which is ideal for AI inference. However, inconsistent and opaque pricing metrics hinder comparisons. This pricing tool compares the cost of services across providers.
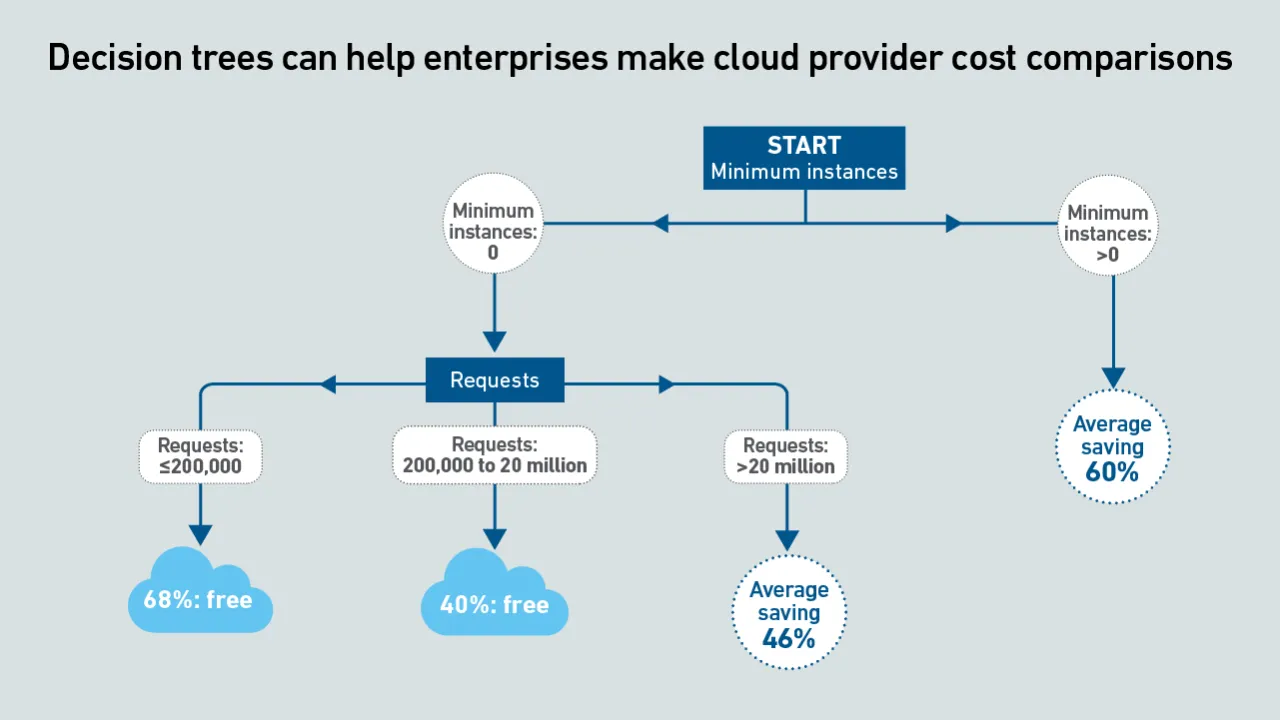
Serverless container services enable rapid scalability, which is ideal for AI inference. However, inconsistent and opaque pricing metrics hinder comparisons. This report uses machine learning to derive clear guidance by means of decision trees.
A report by Uptime's Sustainability and Energy Research Director Jay Dietrich merits close attention; it outlines a way to calculate data center IT work relative to energy consumption. The work is supported by Uptime Institute and The Green Grid.
Today, GPU designers pursue outright performance over power efficiency. This is a challenge for inference workloads that prize efficient token generation. GPU power management features can help, but require more attention.
 Max Smolaks
Max Smolaks
 Daniel Bizo
Daniel Bizo

 John O'Brien
John O'Brien

 Peter Judge
Peter Judge

 Jacqueline Davis
Jacqueline Davis
 Dr. Owen Rogers
Dr. Owen Rogers
 Rose Weinschenk
Rose Weinschenk


 Andy Lawrence
Andy Lawrence